Table of Contents
The sigmoid function in Python is a mathematical function that is used to calculate the probability of an event between 0 and 1. It is a non-linear function that can be calculated using the exp() function from the NumPy library. With this function, the output can be calculated by multiplying the input by the weights and adding the bias. The examples provided will help to illustrate how to calculate a sigmoid function in Python.
A is a mathematical function that has an “S” shaped curve when plotted.
The most common example of a sigmoid function is the logistic sigmoid function, which is calculated as:
F(x) = 1 / (1 + e-x)
The easiest way to calculate a sigmoid function in Python is to use the function from the SciPy library, which uses the following basic syntax:
from scipy.special import expit #calculate sigmoid function for x = 2.5 expit(2.5)
The following examples show how to use this function in practice.
Example 1: Calculate Sigmoid Function for One Value
The following code shows how to calculate the sigmoid function for the value x = 2.5:
from scipy.special import expit #calculate sigmoid function for x = 2.5 expit(2.5) 0.9241418199787566
The value of the sigmoid function for x = 2.5 is 0.924.
We can confirm this by calculating the value manually:
- F(x) = 1 / (1 + e-x)
- F(x) = 1 / (1 + e-2.5)
- F(x) = 1 / (1 + .082)
- F(x) = 0.924
Example 2: Calculate Sigmoid Function for Multiple Values
The following code shows how to calculate the sigmoid function for multiple x values at once:
from scipy.special import expit
#define list of values
values = [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2]
#calculate sigmoid function for each value in list
expit(values)
array([0.11920292, 0.26894142, 0.5, 0.73105858, 0.88079708])
Example 3: Plot Sigmoid Function for Range of Values
The following code shows how to plot the values of a sigmoid function for a range of x values using :
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.special import expit
import numpy as np
#define range of x-values
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
#calculate sigmoid function for each x-value
y = expit(x)
#create plot
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('F(x)')
#display plot
plt.show()
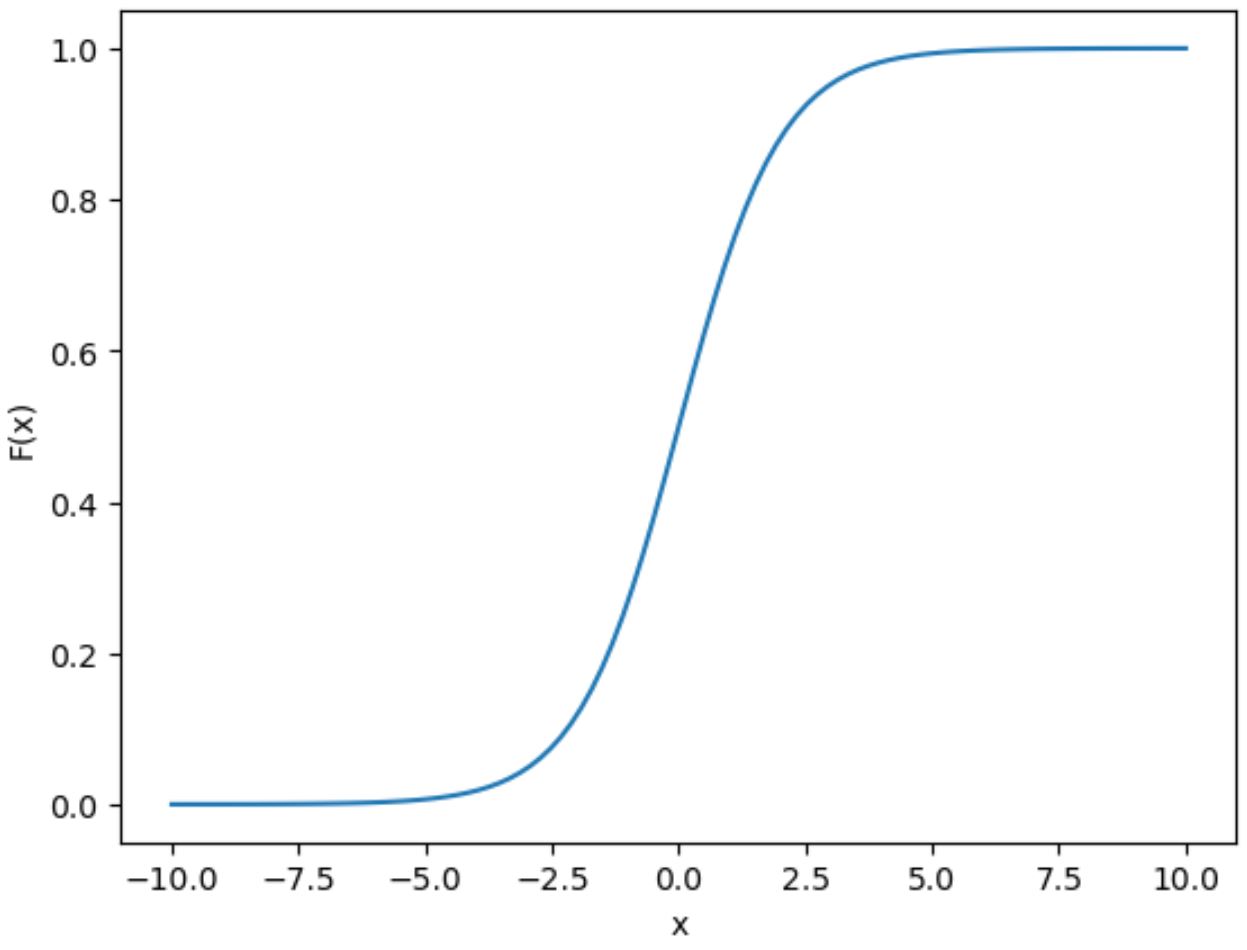
Notice that the plot exhibits the “S” shaped curve that is characteristic of a sigmoid function.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common operations in Python:
