Table of Contents
A two proportion Z-test in SPSS is a statistical analysis used to compare two proportions or percentages from two different groups. It is performed by first entering the data into SPSS and then selecting the “Two Independent Samples” option from the “Analyze” menu. Next, the appropriate variables and confidence level are selected, and the test is run. The result of the test is a p-value, which indicates the likelihood of obtaining the observed difference in proportions by chance. A p-value less than the chosen significance level (usually 0.05) indicates that the difference in proportions is statistically significant. This test is useful in determining if there is a significant difference between two groups, such as the success rates of two different treatments.
A two proportion z-test is used to test for a difference between two population proportions.
The easiest way to perform a two proportion z-test in SPSS is by using Analyze> Descriptive Statistics > Crosstabs.
The following example shows how to do so in practice.
Example: Two Proportion Z-Test in SPSS
Suppose a teacher believes that the proportion of her students in both of her classes who prefer a specific teaching method is equal.
To test this, she surveys the 30 students in each class and receives the following results:
- Class A Size: 30
- Count in Class A who prefer method: 23
- Class B Size: 30
- Count in Class B who prefer method: 18
Here is how to enter this data into SPSS:
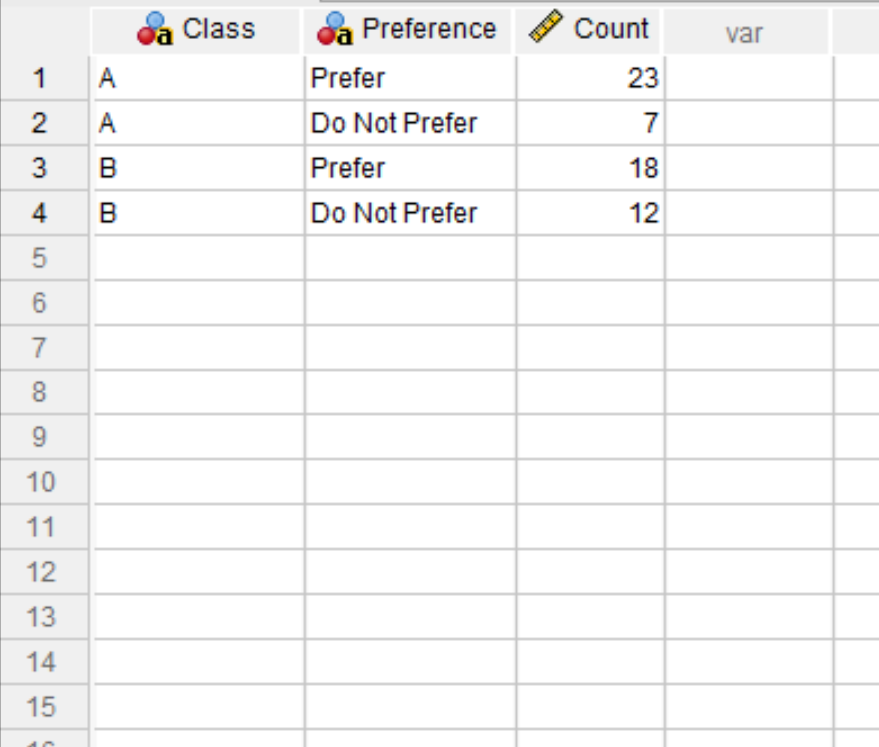
Before we perform the two proportion z-test to determine if the two proportions are equal, we must first weight the cases.
To do so, click the Data tab, then click Weight Cases.
In the new window that appears, drag the Count variable into the Frequency variable panel:
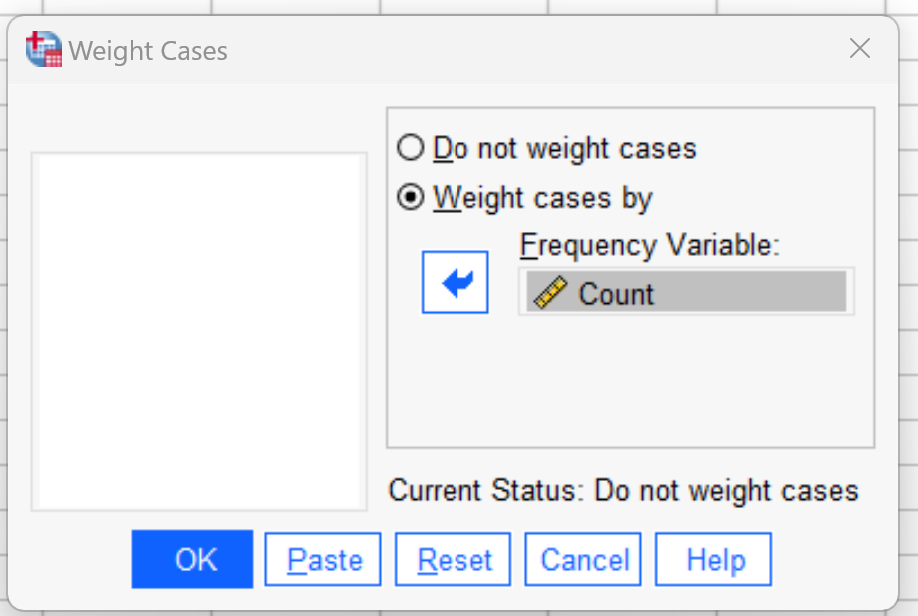
Then click OK.
Then click the Analyze tab, then click Descriptive Statistics, then click Crosstabs:
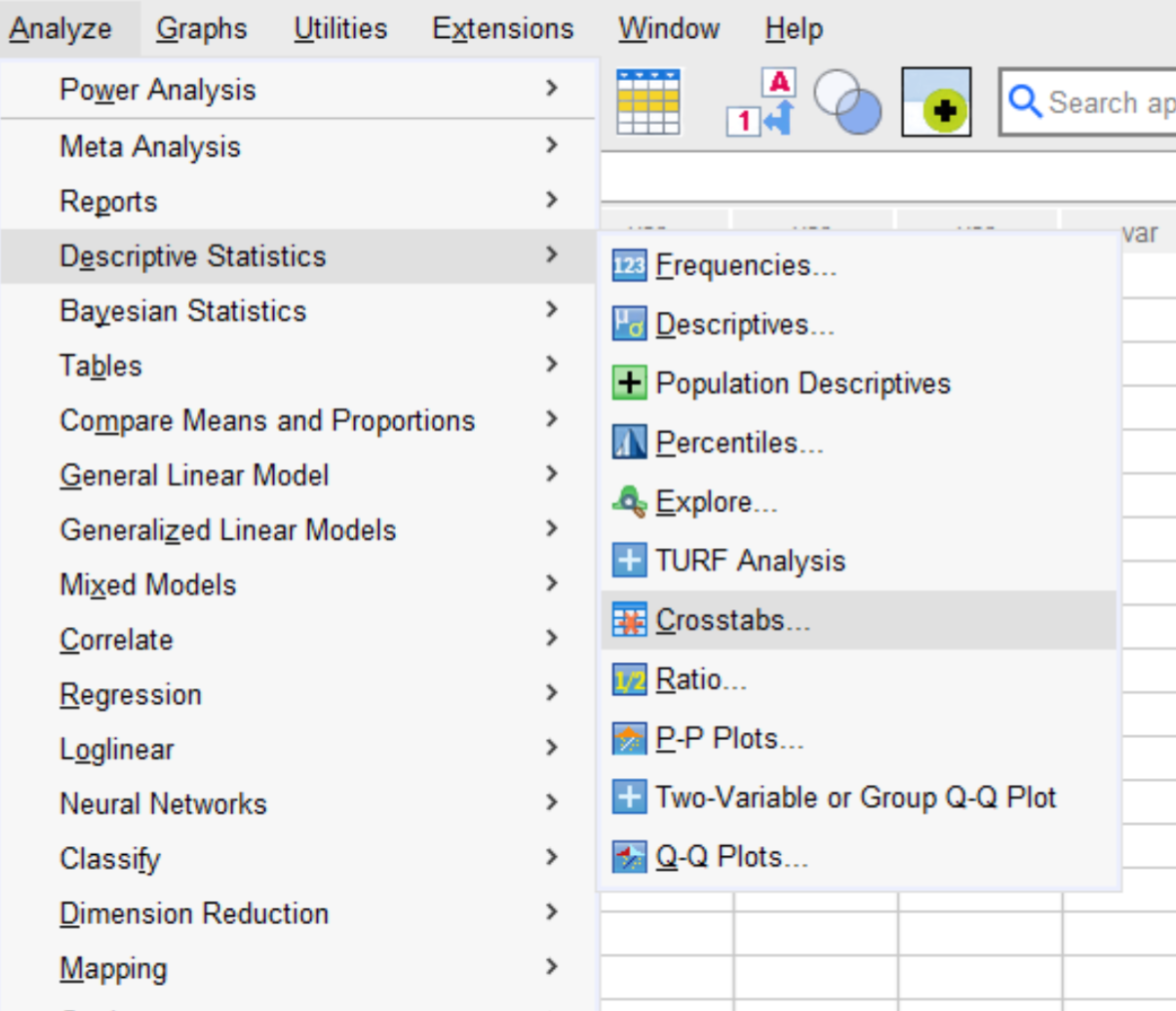
In the new window that appears, drag the Class variable to the Rows panel and drag the Preference variable to the Columns panel:

Then click the Statistics button.
In the new window that appears, check the box next to Chi-square:
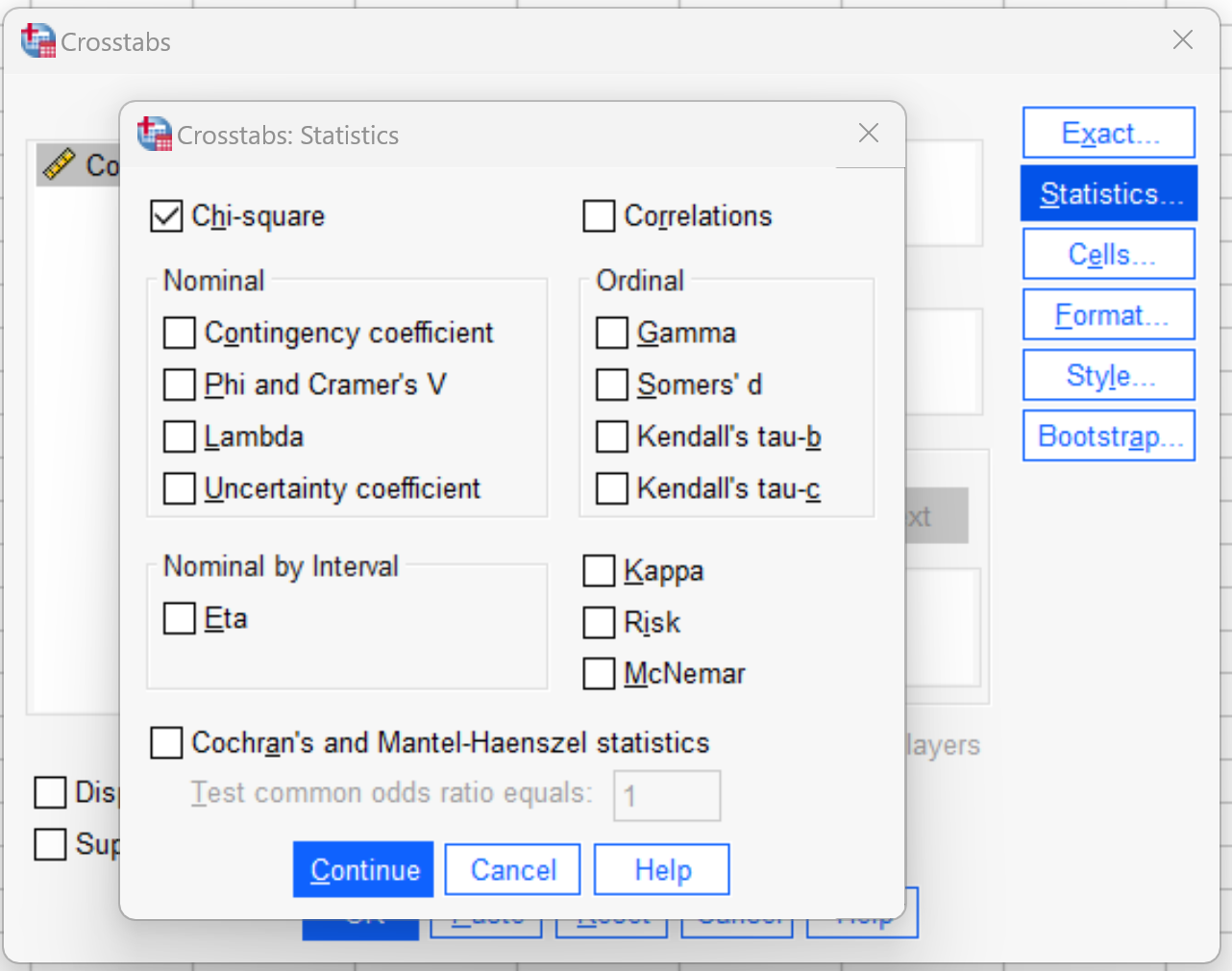
Then click Continue. Then click OK.
The following output will be generated:
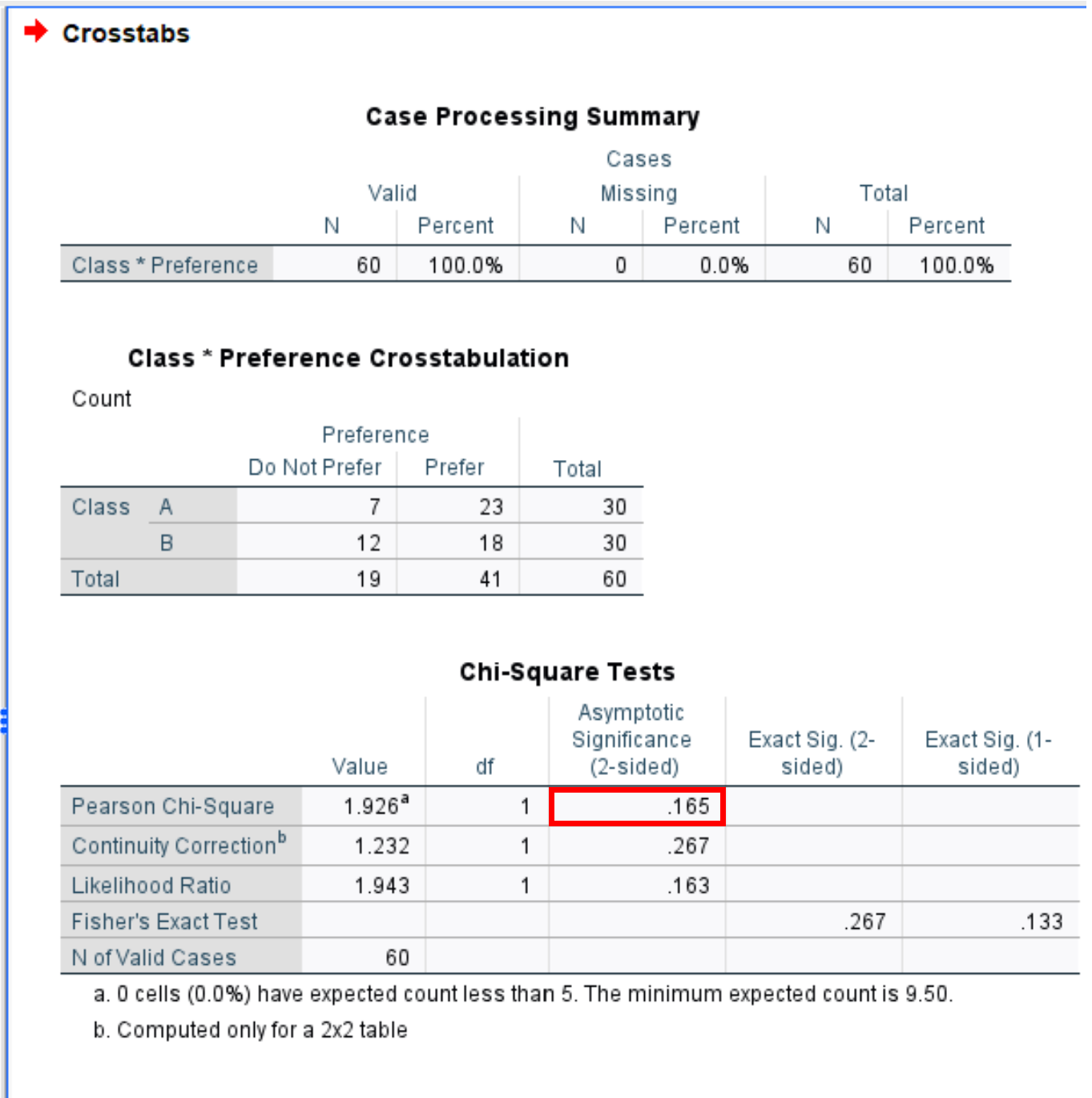
The two-tailed p-value for the two proportion z-test is shown in the final table of the output in the Pearson Chi-Square row.
In this particular example the p-value for the two proportion z-test is .165.
The two proportion z-test uses the following hypotheses:
- H0: The two population proportions are equal.
- HA: The two population proportions are not equal.
Since our p-value (.165) is less than .05, we fail to the null hypothesis.
Thus, we do not have sufficient evidence to say that the proportion of students in each class who prefer the specific teaching method is different.
Bonus: You can also use the arabpsychology .
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SPSS:
