Table of Contents
To conduct a one sample t-test in Excel, you need to first enter the data into the worksheet. Next, open the Data Analysis tool in the Data tab and select the t-test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances option. Input the data range and the confidence level you desire, then click OK to generate the results. The output will appear in a new spreadsheet, which will provide you with the t-test statistic, the p-value, and the mean difference. The p-value tells you if there is a statistically significant difference between the sample data and the hypothesized mean.
A is used to test whether or not the mean of a population is equal to some value.
This tutorial explains how to conduct a one sample t-test in Excel.
How to Conduct a One Sample t-Test in Excel
Suppose a botanist wants to know if the mean height of a certain species of plant is equal to 15 inches. She collects a random sample of 12 plants and records each of their heights in inches.
The following image shows the height (in inches) for each plant in the sample:
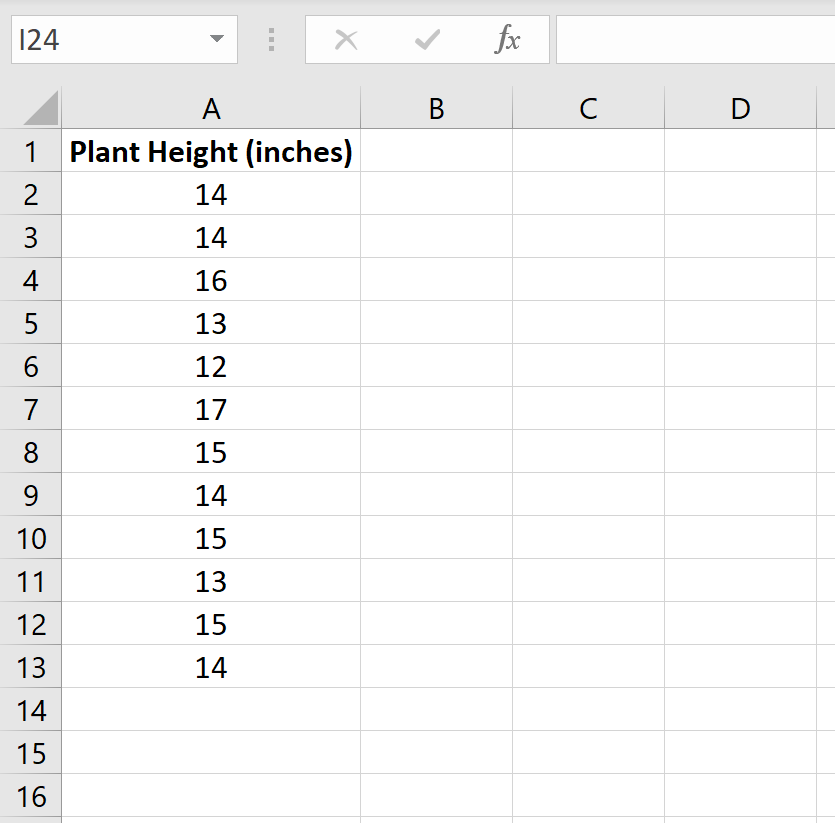
We can use the following steps to conduct a one sample t-test to determine if the mean height for this species of plant is actually equal to 15 inches.
Step 1: Find the sample size, sample mean, and sample standard deviation.
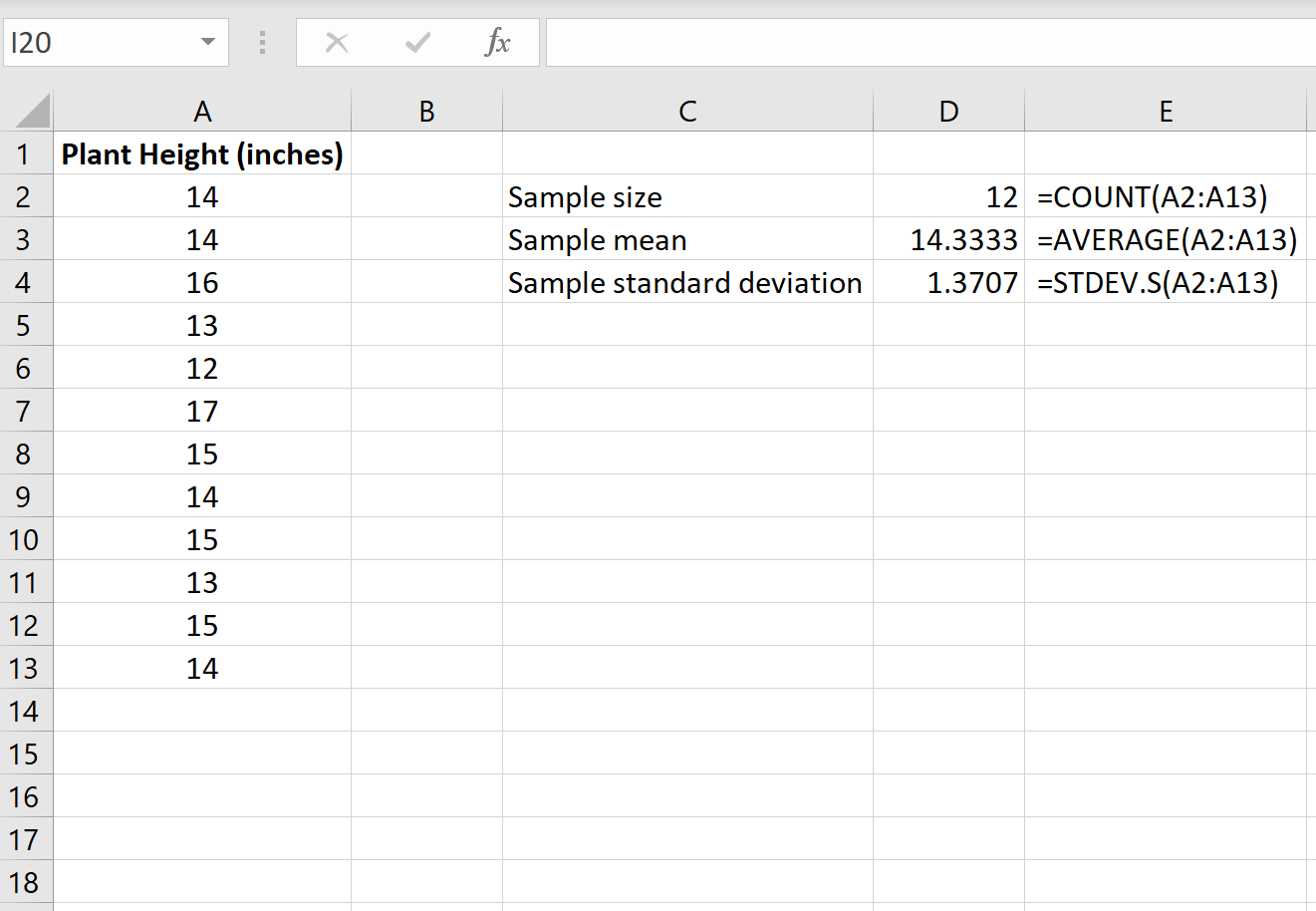
First, we need to find the sample size, sample mean, and sample standard deviation, which will all be used to conduct the one sample t-test.
The following image shows the formulas we can use to calculate these values:
Step 2: Calculate the test statistic t.
Next, we will calculate the test statistic t using the following formula:
t = x – µ / (s/√n)
where:
x = sample mean
µ = hypothesized population mean
n = sample size
The following image shows how to calculate t in Excel:
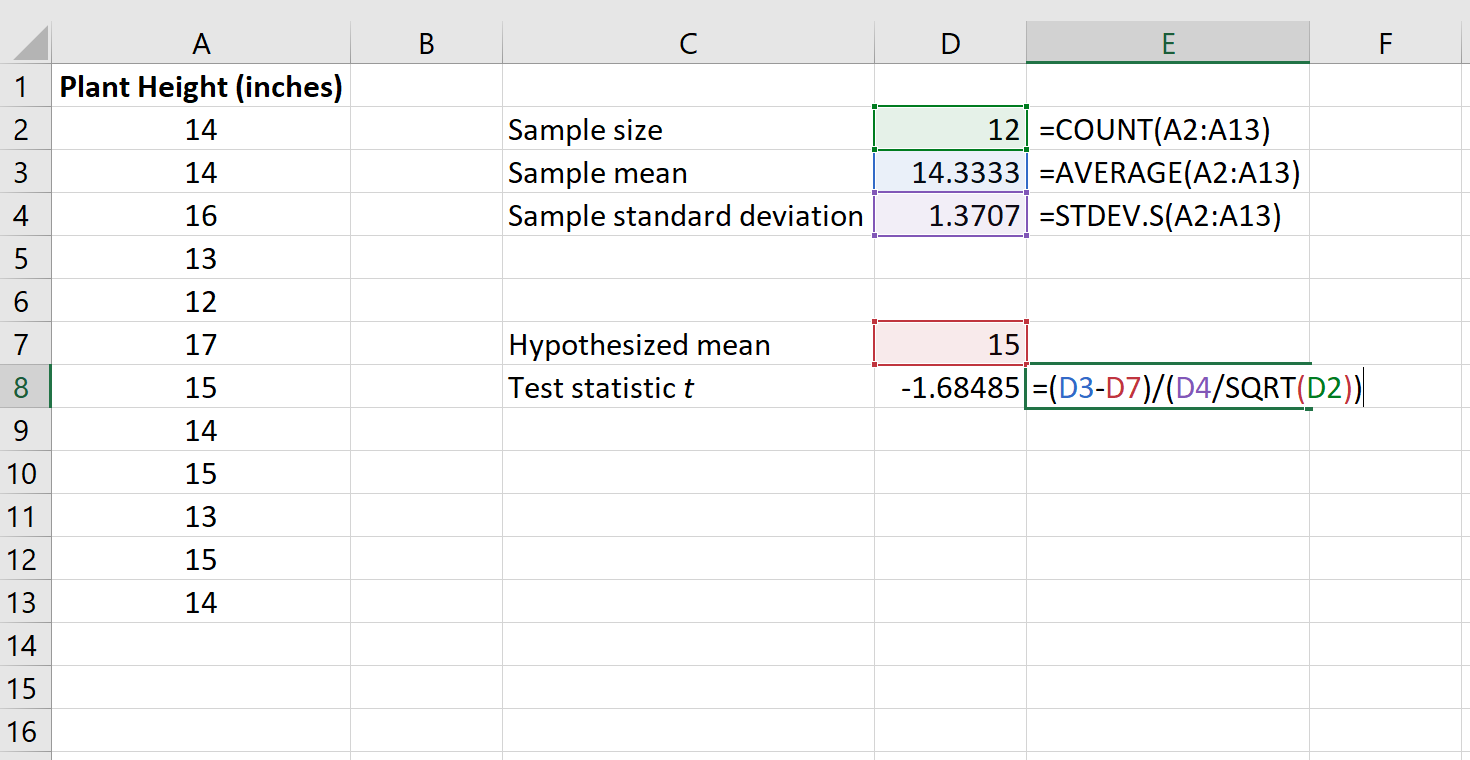
The test statistic t turns out to be -1.68485.
Step 3: Calculate the p-value of the test statistic.
Next, we need to calculate the p-value associated with the test statistic using the following function in Excel:
=T.DIST.2T(ABS(x), deg_freedom)
where:
x = test statistic t
deg_freedom = degrees of freedom for the test, which is calculated as n-1
Technical Notes:
The function T.DIST.2T() returns the p-value for a two-tailed t-test. If you’re instead conducting a left-tailed t-test or a right-tailed t-test, you would instead use the functions T.DIST() or T.DIST.RT(), respectively.
The following image shows how to calculate the p-value for our test statistic:
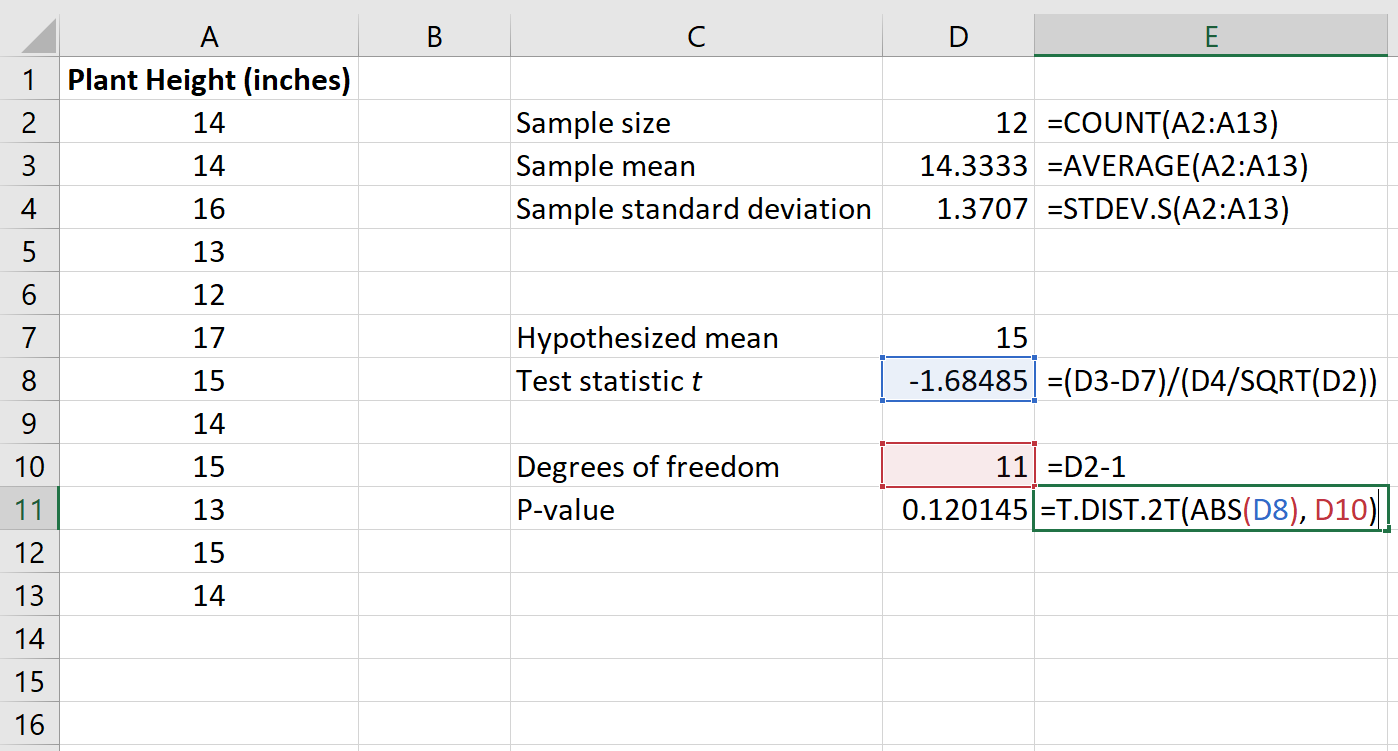
The p-value turns out to be 0.120145.
Step 4: Interpret the results.
The two hypotheses for this particular one sample t test are as follows:
H0: µ = 15 (the mean height for this species of plant is 15 inches)
HA: µ ≠15 (the mean height is not 15 inches)
Because the p-value of our test (0.120145) is greater than alpha = 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis of the test.
We do not have sufficient evidence to say that the mean height for this particular species of plant is different from 15 inches.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common types of t-tests in Excel:
How to Conduct a Two Sample t-Test in Excel
How to Conduct a Paired Samples t-Test in Excel
