Table of Contents
R-Squared, also known as the coefficient of determination, is a statistical measure used to determine the strength and relationship between two variables in a regression model. It is often used in data analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of a regression model in explaining the variability of the data points.
To calculate R-Squared in Excel, you can use the built-in function “RSQ” or the “Data Analysis” tool. The RSQ function requires two arrays of data, representing the x and y variables, and will return the R-Squared value. The Data Analysis tool allows you to perform a regression analysis and displays the R-Squared value in the output.
For example, if we have a dataset of monthly sales and advertising expenses, we can use R-Squared to determine the extent to which advertising expenses affect the sales. A high R-Squared value close to 1 indicates a strong positive relationship between the two variables, while a low value close to 0 indicates a weak or no relationship.
In another scenario, if we have a dataset of student’s study hours and exam scores, we can use R-Squared to evaluate how well the study hours predict the exam scores. A high R-Squared value would indicate that the study hours are a good predictor of the exam scores.
In conclusion, calculating R-Squared in Excel can help us understand the strength and relationship between two variables in a regression model. It is a useful tool in data analysis and can provide valuable insights for decision making.
Calculate R-Squared in Excel (With Examples)
R-squared, often written as r2, is a measure of how well a fits a dataset.
In technical terms, it is the proportion of the variance in the response variable that can be explained by the predictor variable.
The value for r2 can range from 0 to 1:
- A value of 0 indicates that the response variable cannot be explained by the predictor variable at all.
- A value of 1 indicates that the response variable can be perfectly explained without error by the predictor variable.
Related:
This tutorial explains how to calculate r2 for two variables in Excel.
Example: Calculating R-Squared in Excel
Suppose we have the following data for the number of hours studied and the exam score received for 20 students:

Now suppose we are interested in fitting a simple linear regression model to this data, using “hours” as the predictor variable and “score” as the response variable.
To find the r2 for this data, we can use the RSQ() function in Excel, which uses the following syntax:
=RSQ(known_ys, known_xs)
where:
- known_ys: the values for the response variable
- known_xs: the values for the predictor variable
Here’s what that formula looks like in our example:
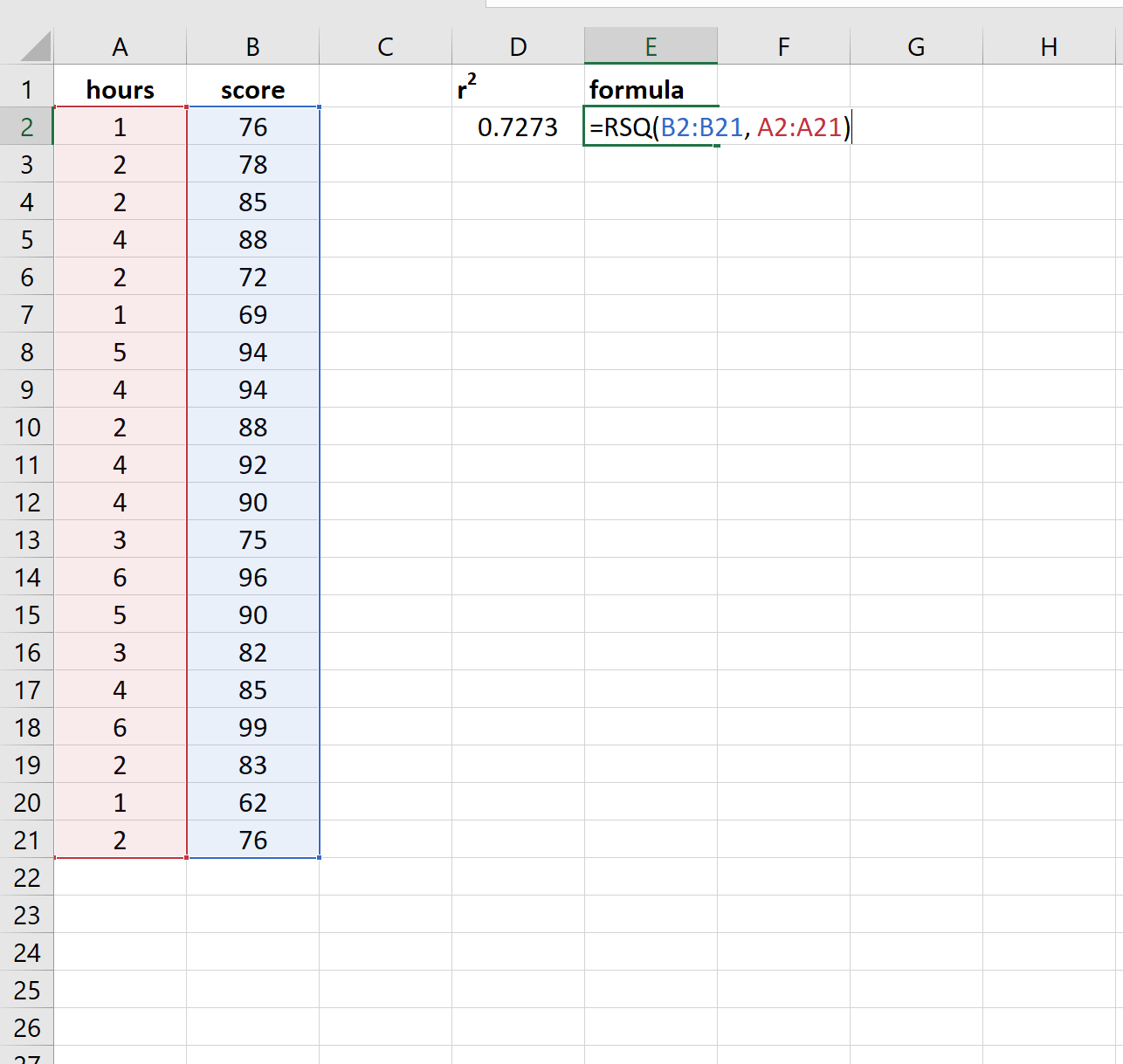
In this example, 72.73% of the variation in the exam scores can be explained by the number of hours studied.

Notice that the R Square value in the first table is 0.7273, which matches the result that we got using the RSQ() function.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in Excel:
