Table of Contents
The process of ignoring #N/A values when using formulas in Excel involves utilizing the IFERROR function. This function allows you to specify an alternate value or action when an #N/A error is encountered within a formula. By using this function, you can effectively bypass the #N/A values and continue with the desired calculation. This is particularly useful when working with large data sets or when performing complex calculations in Excel. By ignoring #N/A values, you can ensure that your formulas accurately reflect the intended results without being disrupted by errors.
Ignore #N/A Values When Using Formulas in Excel
You can use the following basic syntax to calculate the mean, median, sum, standard deviation, etc. in Excel while ignoring #N/A values:
=AVERAGE(IFNA(A2:A21, "")) =MEDIAN(IFNA(A2:A21, "")) =SUM(IFNA(A2:A21, "")) =STDEV(IFNA(A2:A21, ""))
This syntax simply replaces #N/A values with blanks and then calculates the descriptive statistic you’re interested in.
The following examples show how to use this syntax in practice.
Example 1: Calculate Mean & Ignore #N/A Values
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the mean of a dataset that contains #N/A values:
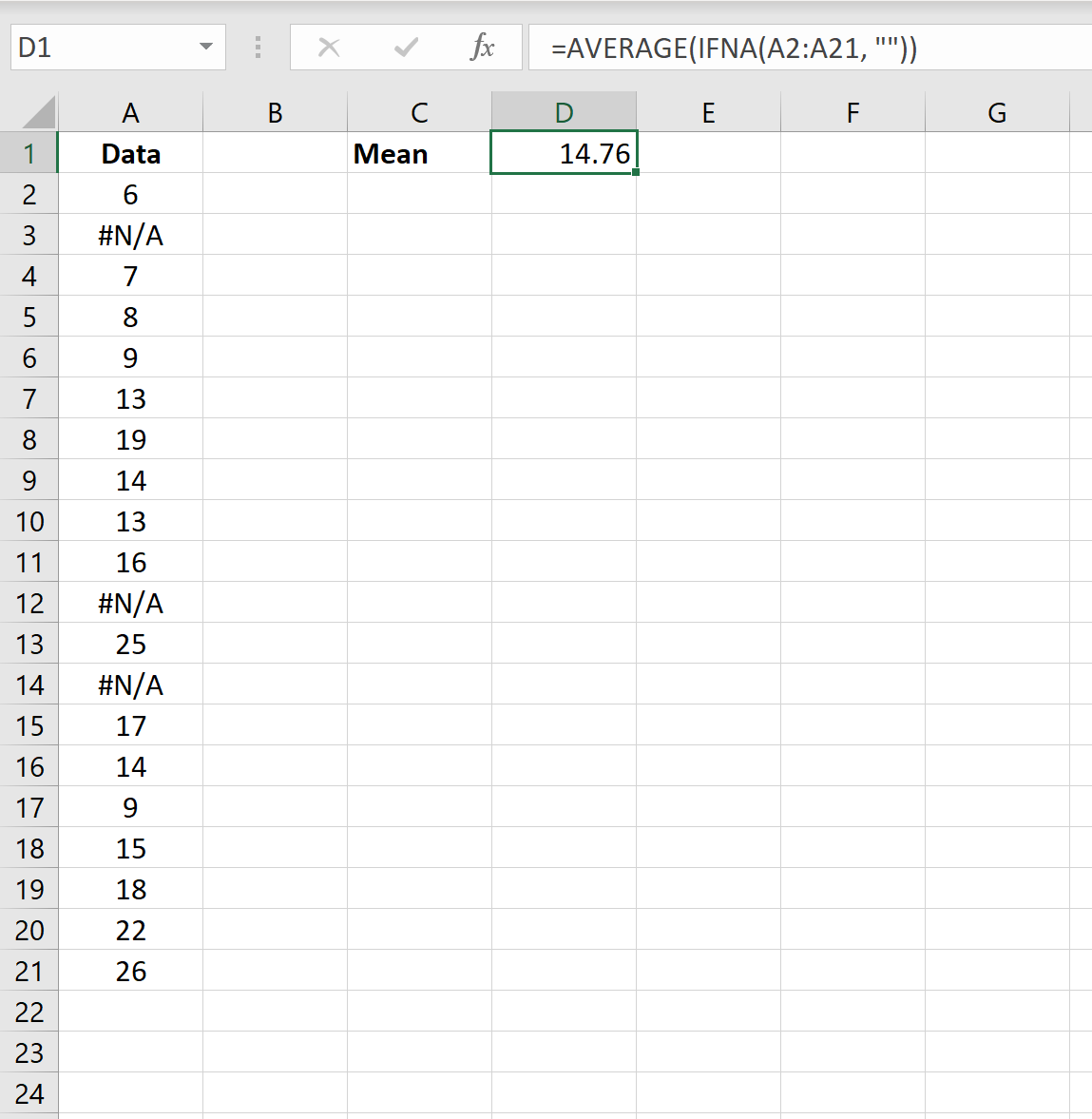
The mean of the dataset (ignoring all #N/A values) is 14.76.
Example 2: Calculate Median & Ignore #N/A Values
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the median of a dataset that contains #N/A values:
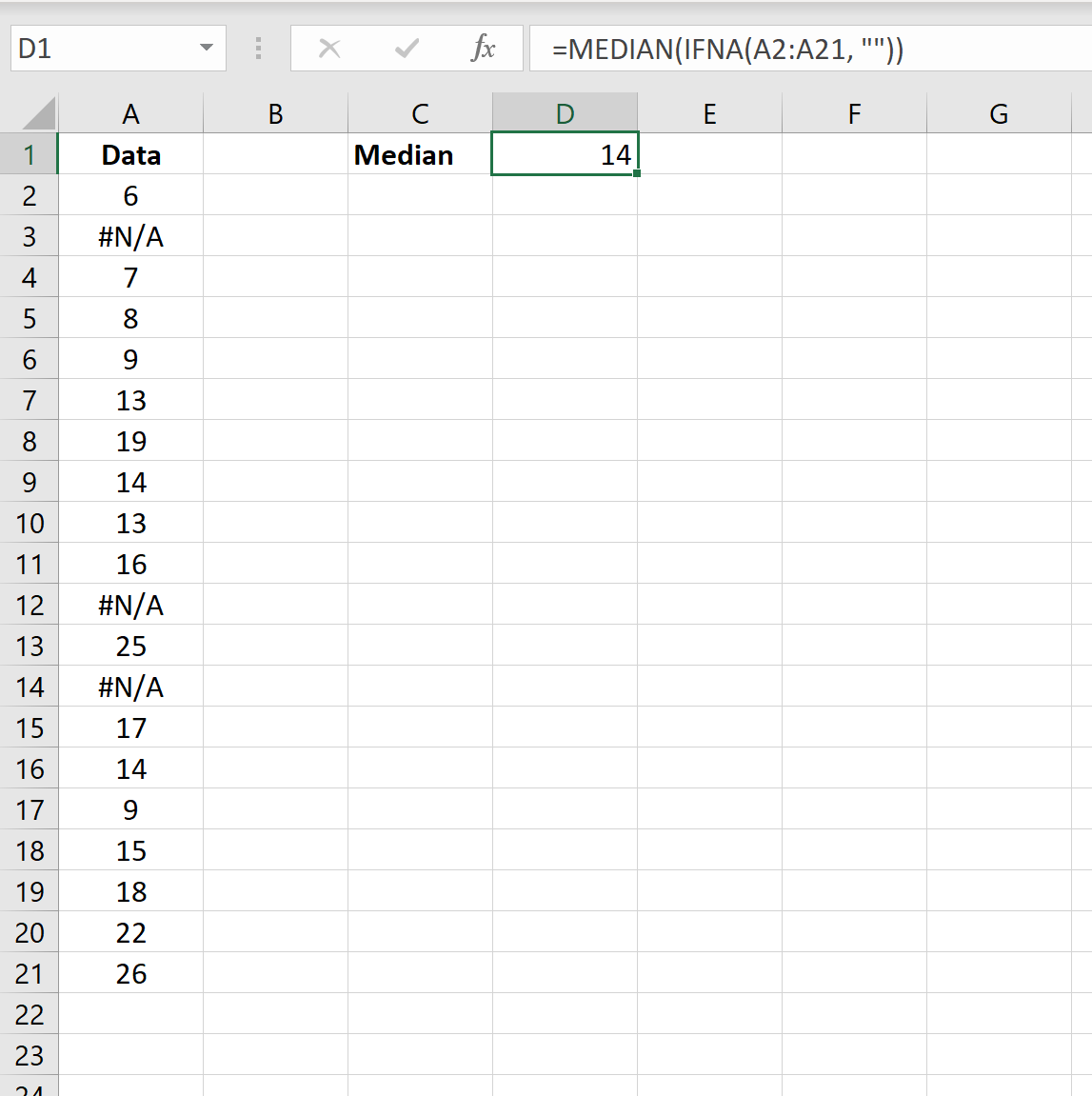
The median of the dataset (ignoring all #N/A values) is 14.
Example 3: Calculate Sum & Ignore #N/A Values
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the sum of a dataset that contains #N/A values:
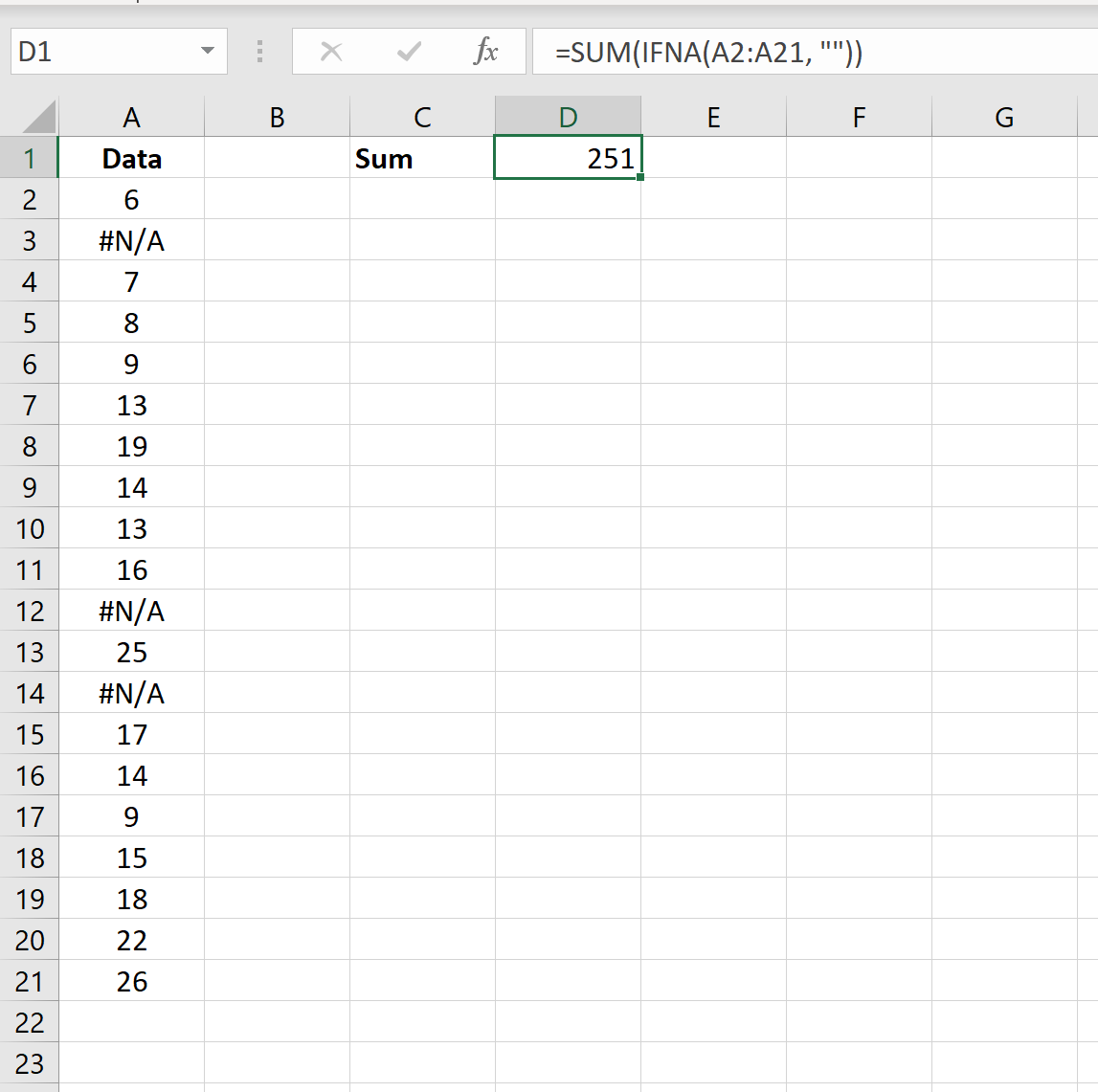
The sum of the dataset (ignoring all #N/A values) is 251.
Example 4: Calculate Standard Deviation & Ignore #N/A Values
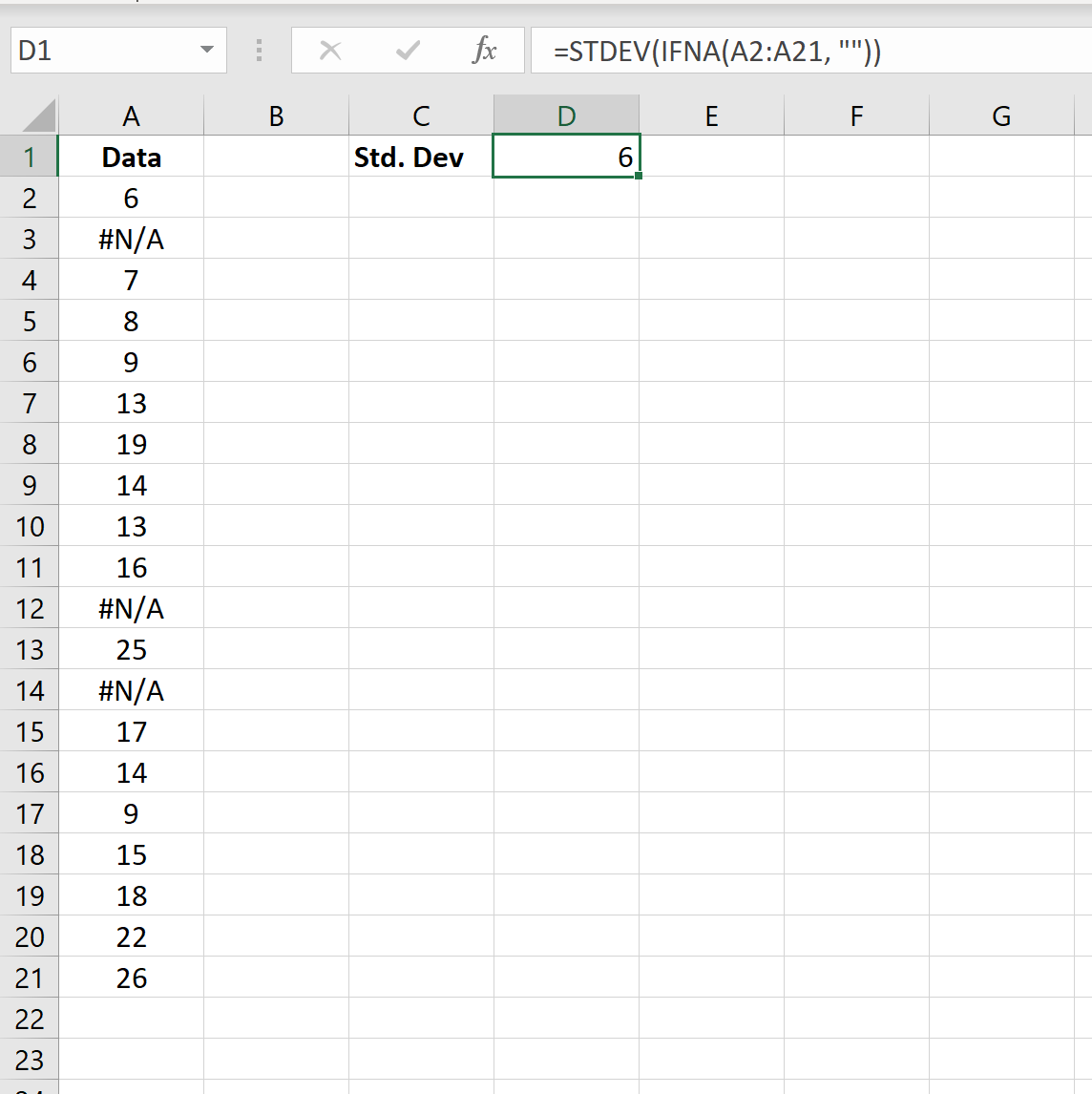
The standard deviation of the dataset (ignoring all #N/A values) is 6.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in Excel:
