Table of Contents
In order to find the T critical value in Excel, you can use the “T.INV” function. This function takes in two arguments: the probability level and the degrees of freedom. The probability level is typically set at 0.05, which represents a confidence level of 95%. The degrees of freedom can be calculated by subtracting 1 from the sample size. By inputting these values into the function, Excel will return the T critical value for that specific probability level and degrees of freedom. This value can then be used for statistical calculations or to determine the rejection region for a T-test.
Find the T Critical Value in Excel
Whenever you conduct a t-test, you will get a test statistic as a result. To determine if the results of the t-test are statistically significant, you can compare the test statistic to a T critical value. If the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than the T critical value, then the results of the test are statistically significant.
The T critical value can be found by using a or by using statistical software.
To find the T critical value, you need to specify:
- A significance level (common choices are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10)
- The degrees of freedom
- The type of test (one-tailed or two-tailed)
Using these three values, you can determine the T critical value to be compared with the test statistic.
Related:
How to Find the T Critical Value in Excel
Excel offers two functions to find the T critical value.
T.INV
To find the T critical value in Excel for a one-tailed test, you can use the T.INV.() function, which uses the following syntax:
T.INV(probability, deg_freedom)
- probability: The significance level to use
- deg_freedom: The degrees of freedom
This function returns the critical value from the t distribution for a one-tailed test based on the significance level and the degrees of freedom provided.
T.INV.2T
To find the T critical value in Excel for a two-tailed test, you can use the T.INV.2T() function, which uses the following syntax:
T.INV.2T(probability, deg_freedom)
- probability: The significance level to use
- deg_freedom: The degrees of freedom
Examples of Finding the T Critical Value in Excel
The following examples illustrate how to find the T critical value for a left-tailed test, right-tailed test, and a two-tailed test.
Left-tailed test
To find the T critical value for a left-tailed test with a significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11, we can type the following formula into Excel: T.INV(0.05, 11)
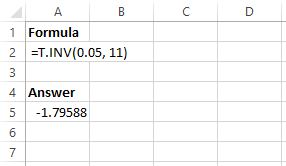
This returns the value -1.79588. This is the critical value for a left-tailed test with significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11.
Right-tailed test
To find the T critical value for a right-tailed test with a significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11, we can type the following formula into Excel: ABS(T.INV(0.05, 11))

This returns the value 1.79588. This is the critical value for a two-tailed test with significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11.
Two-tailed test
To find the T critical value for a two-tailed test with a significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11, we can type the following formula into Excel: T.INV.2T(0.05, 11)

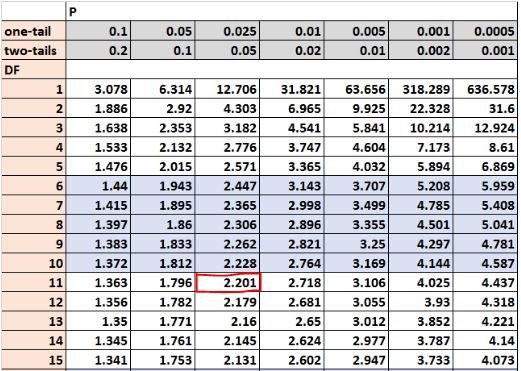
This returns the value 2.200985. This is the critical value for a two-tailed test with significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11.
Note that this also matches the number we would find in the with α = 0.05 for two tails and DF (degrees of freedom) = 11.
Cautions on Finding the T Critical Value in Excel
Note that both the T.INV() and T.INV.2T() functions in Excel will throw an error if any of the following occur:
- If any argument is non-numeric.
- If the value for probability is less than zero or greater than 1.
- If the value for deg_freedom is less than 1.
