Table of Contents
The Shapiro-Wilk Test is a statistical test used to determine if a given data set follows a normal distribution. To perform this test in SPSS, first open the data set you want to test. Then, go to “Analyze” and select “Nonparametric Tests” followed by “Legacy Dialogs” and “Explore”. In the “Explore” dialog box, select the variable you want to test and click on “Plots”. Check the box next to “Normality plots with tests” and select “Shapiro-Wilk” from the drop-down menu. Finally, click “Continue” and then “OK” to run the test and view the results in the output window.
The Shapiro-Wilk test is a statistical that is used to determine whether or not given dataset follows a .
The Shapiro-Wilk test uses the following hypotheses:
- H0: The data is normally distributed.
- HA: The data is not normally distributed.
If the that results from the test is less than your chosen significance level (e.g. 0.05) then you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the data is not normally distributed.
To perform a Shapiro-Wilk test in SPSS, you can use Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Explore.
The following example shows how to perform this test in practice.
Example: How to Perform a Shapiro-Wilk Test in SPSS
Suppose we have the following dataset in SPSS that contains information about the final exam scores received by 25 different students in some class:
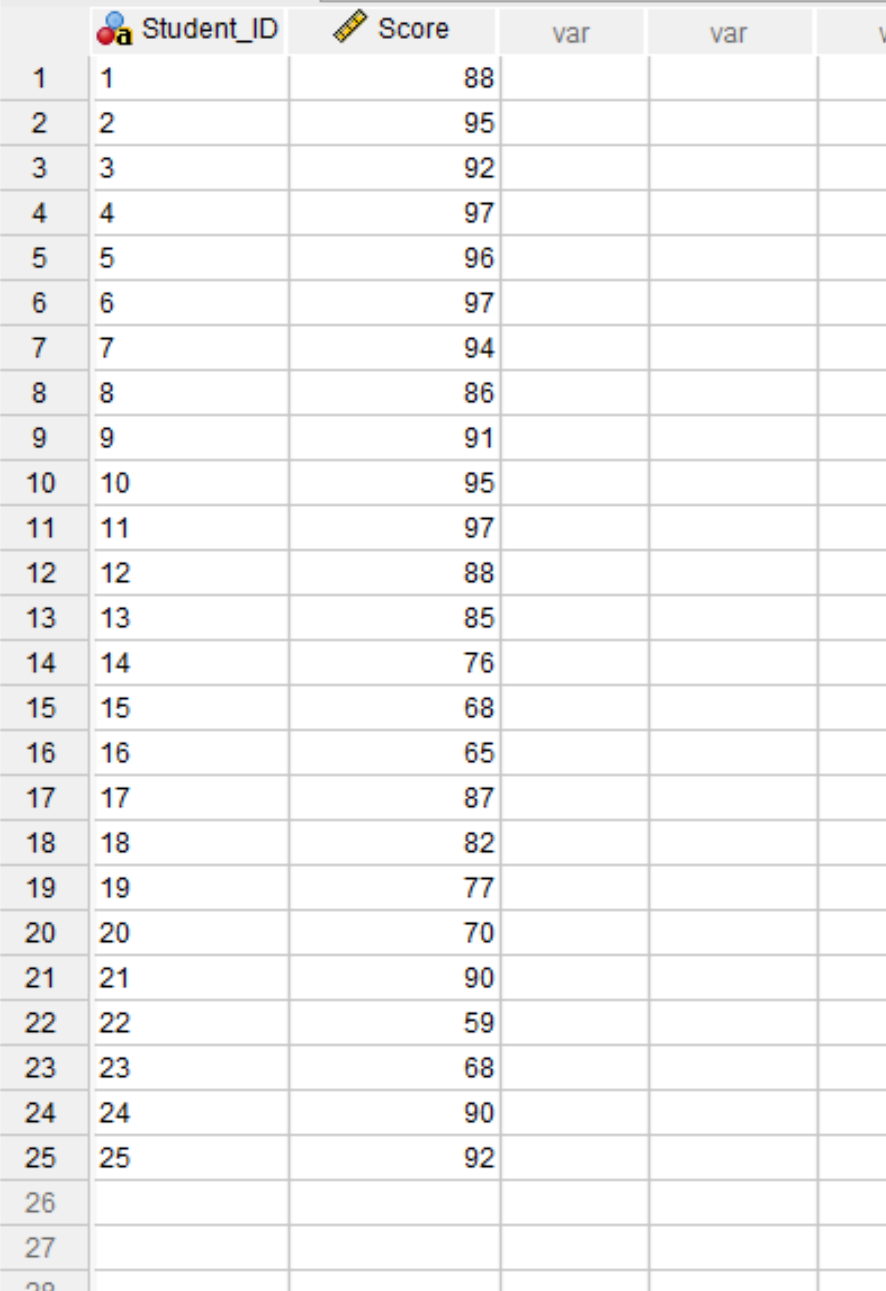
Suppose that we would like to perform a Shapiro-Wilk test to determine if the exam scores are normally distributed.
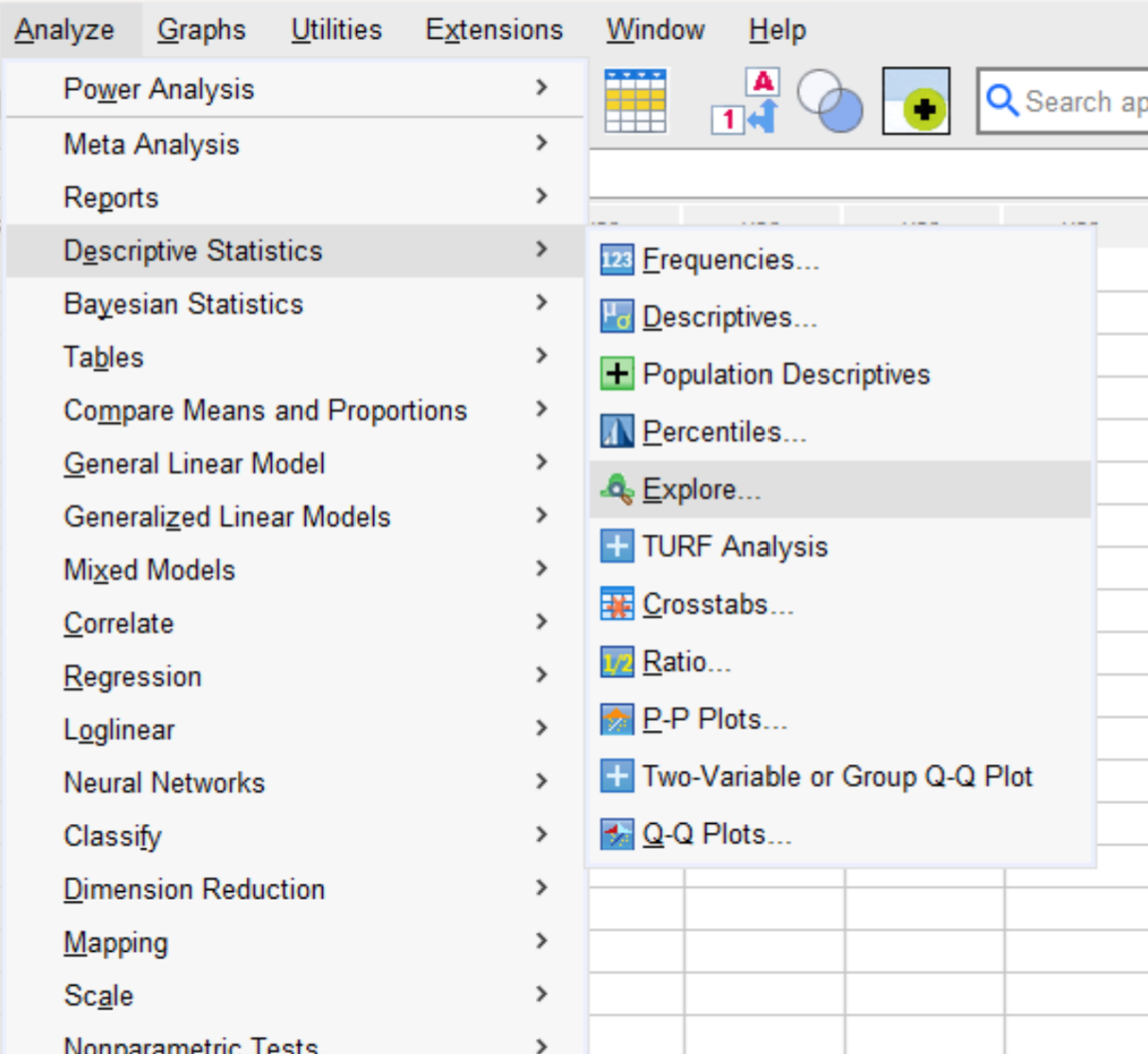
To do so, click the Analyze tab, then click Descriptive Statistics, then click Explore:
In the new window that appears, drag the Score variable into the Dependent List panel:
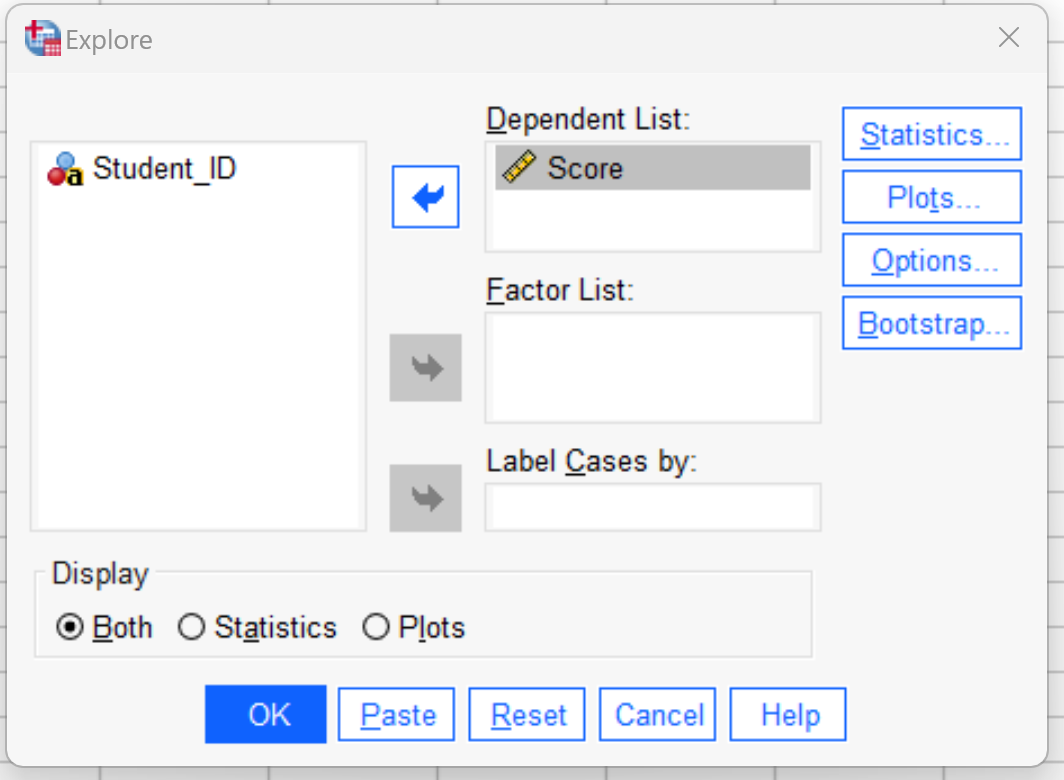
Then click the Plots button.
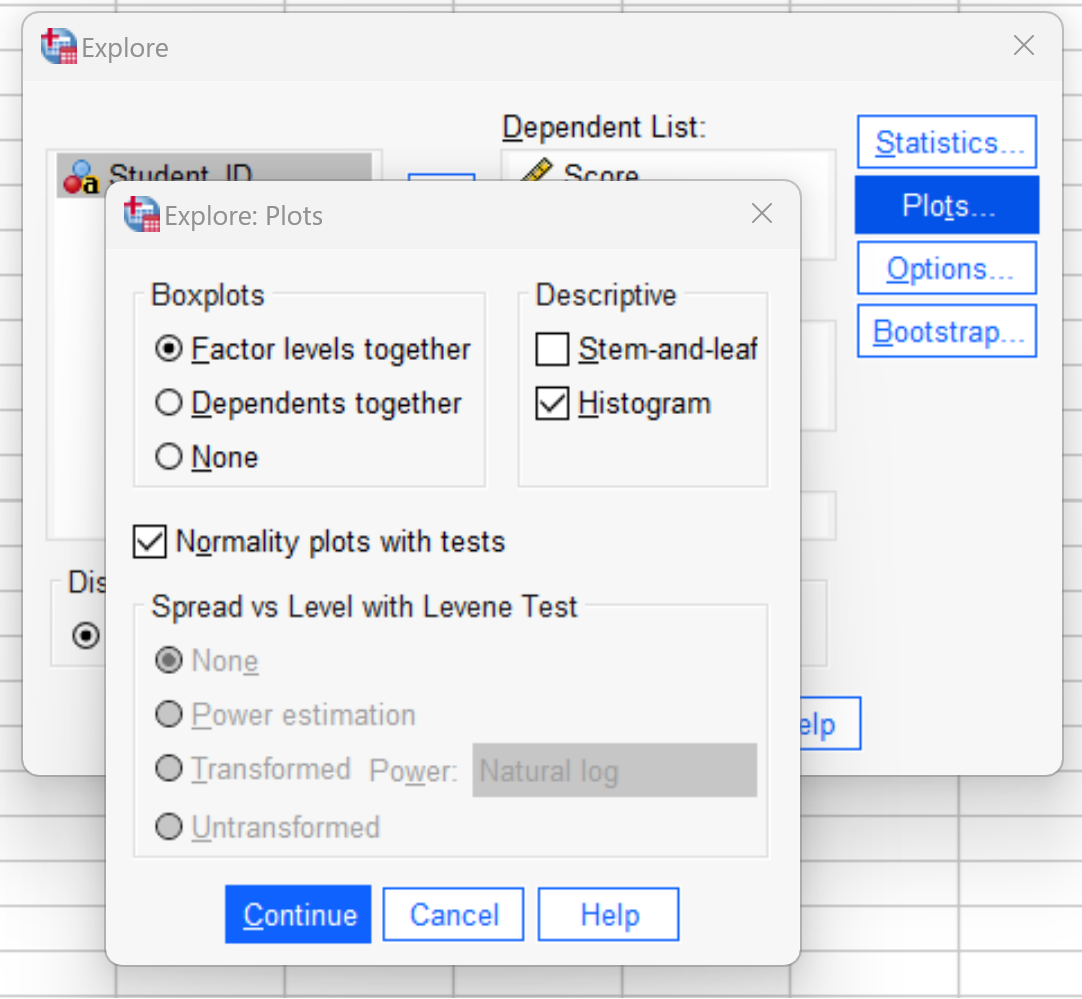
Check the box next to Histogram and Normality plots with tests:
The following output will be generated that shows the results of the Shapiro-Wilk test along with a histogram that displays the distribution of exam scores:
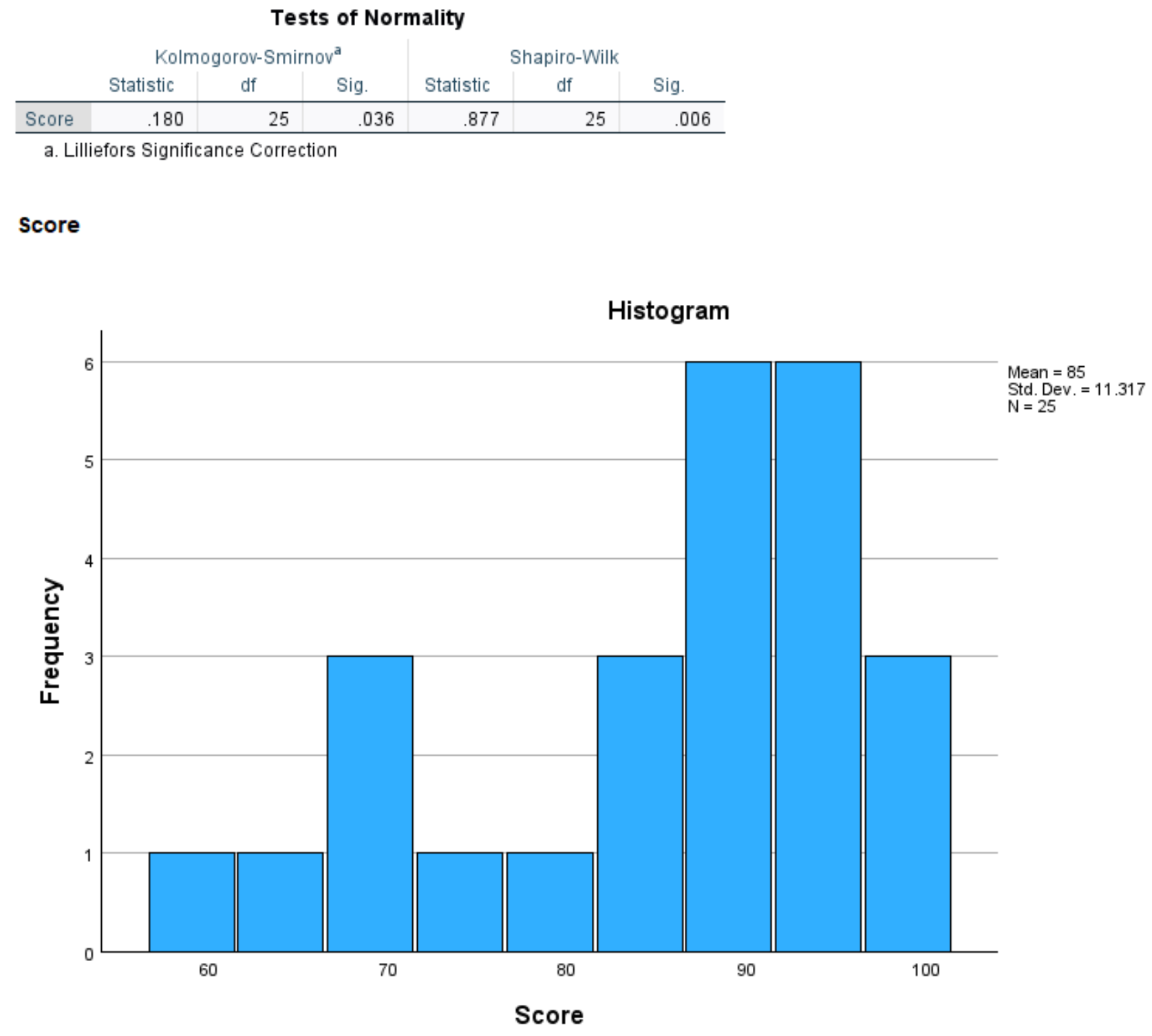
From the output we can see that the p-value of the Shapiro-Wilk test is .006.
Recall that the Shapiro-Wilk test uses the following hypotheses:
- H0: The data is normally distributed.
- HA: The data is not normally distributed.
Since the p-value of the test is less than .05, we have sufficient evidence to the null hypothesis.
Thus, we would conclude that the distribution of exam scores is not normally distributed.
From looking at the histogram, it’s also clear that this distribution of exam scores does not follow a typical “bell curve” that is associated with a normal distribution.
The distribution of exam scores appear to be , with the “tail” of the distribution extending towards the left side of the graph.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common operations in SPSS:
