Posttraumatic stress disorder (also known as post-traumatic stress disorder or PTSD) is a severe anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to any event that results in psychological trauma. This event may involve the threat of death to oneself or to someone else, or to one’s own or someone else’s physical, sexual, or psychological integrity, overwhelming the individual’s ability to cope. As an effect of psychological trauma, PTSD is less frequent and more enduring than the more commonly seen acute stress response.
Diagnostic symptoms for PTSD include re-experiencing the original trauma(s) through flashbacks or nightmares, avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma, and increased arousal – such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, anger, and hypervigilance. Formal diagnostic criteria (both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10) require that the symptoms last more than one month and cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Classification
Posttraumatic stress disorder is classified as an anxiety disorder, characterized by aversive anxiety-related experiences, behaviors, and physiological responses that develop after exposure to a psychologically traumatic event (sometimes months after). Its features persist for longer than 30 days, which distinguishes it from the briefer acute stress disorder. These persisting posttraumatic stress symptoms cause significant disruptions of one or more important areas of life function. It has three sub-forms: acute, chronic, and delayed-onset.
Causes
Psychological trauma
PTSD is believed to be caused by either physical trauma or psychological trauma, or more frequently a combination of both. According to Atkinson et al. (2000) PTSD is more likely to be caused by physical or psychological trauma caused by humans such as rape, war, or terrorist attack than trauma caused by natural disasters. Possible sources of trauma include experiencing or witnessing childhood or adult physical, emotional or sexual abuse. In addition, experiencing or witnessing an event perceived as life-threatening such as physical assault, adult experiences of sexual assault, accidents, drug addiction, illnesses, medical complications, or employment in occupations exposed to war (such as soldiers) or disaster (such as emergency service workers).
Traumatic events that may cause PTSD symptoms to develop include violent assault, kidnapping, sexual assault, torture, being a hostage, prisoner of war or concentration camp victim, experiencing a disaster, violent automobile accidents or getting a diagnosis of a life-threatening illness. Children or adults may develop PTSD symptoms by experiencing bullying or mobbing. Preliminary research suggests that child abuse may interact with mutations in a stress-related gene to increase the risk of PTSD in adults.
Multiple studies show that parental PTSD and other posttraumatic disturbances in parental psychological functioning can, despite a traumatized parent’s best efforts, interfere with their response to their child as well as their child’s response to trauma. Parents with violence-related PTSD may, for example, inadvertently expose their children to developmentally inappropriate violent media due to their need to manage their own emotional dysregulation. Clinical findings indicate that a failure to provide adequate treatment to children after they suffer a traumatic experience, depending on their vulnerability and the severity of the trauma, will ultimately lead to PTSD symptoms in adulthood.
Neuroendocrinology
PTSD symptoms may result when a traumatic event causes an overactive adrenaline response, which creates deep neurological patterns in the brain. These patterns can persist long after the event that triggered the fear, making an individual hyper-responsive to future fearful situations.
PTSD displays biochemical changes in the brain and body that differ from other psychiatric disorders such as major depression. Individuals diagnosed with PTSD respond more strongly to a dexamethasone suppression test than individuals diagnosed with clinical depression.
In addition, most people with PTSD also show a low secretion of cortisol and high secretion of catecholamines in urine, with a norepinephrine/cortisol ratio consequently higher than comparable non-diagnosed individuals. This is in contrast to the normative fight-or-flight response, in which both catecholamine and cortisol levels are elevated after exposure to a stressor.
Brain catecholamine levels are low, and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) concentrations are high. Together, these findings suggest abnormality in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Given the strong cortisol suppression to dexamethasone in PTSD, HPA axis abnormalities are likely predicated on strong negative feedback inhibition of cortisol, itself likely due to an increased sensitivity of glucocorticoid receptors. Some researchers have associated the response to stress in PTSD with long-term exposure to high levels of norepinephrine and low levels of cortisol, a pattern associated with improved learning in animals.
Translating this reaction to human conditions gives a pathophysiological explanation for PTSD by a maladaptive learning pathway to fear response through a hypersensitive, hyperreactive and hyperresponsive HPA axis.
Low cortisol levels may predispose individuals to PTSD: Following war trauma, Swedish soldiers serving in Bosnia and Herzegovina with low pre-service salivary cortisol levels had a higher risk of reacting with PTSD symptoms, following war trauma, than soldiers with normal pre-service levels. Because cortisol is normally important in restoring homeostasis after the stress response, it is thought that trauma survivors with low cortisol experience a poorly contained—that is, longer and more distressing—response, setting the stage for PTSD.
However, there is considerable controversy within the medical community regarding the neurobiology of PTSD. A review of existing studies on this subject showed no clear relationship between cortisol levels and PTSD. Only a slight majority have found a decrease in cortisol levels while others have found no effect or even an increase.
Neuroanatomy
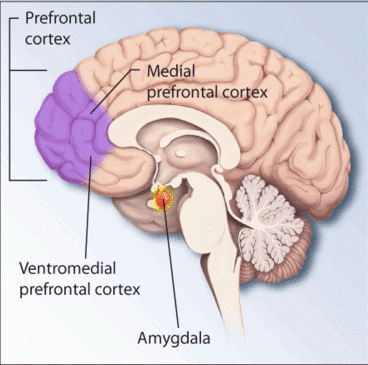
Regions of the brain associated with stress and posttraumatic stress disorder
Three areas of the brain whose function may be altered in PTSD have been identified: the prefrontal cortex, amygdala and hippocampus. Much of this research has utilised PTSD victims from the Vietnam War. For example, a prospective study using the Vietnam Head Injury Study showed that damage to the prefrontal cortex may actually be protective against later development of PTSD. In a study by Gurvits et al., combat veterans of the Vietnam War with PTSD showed a 20% reduction in the volume of their hippocampus compared with veterans who suffered no such symptoms. This finding could not be replicated in chronic PTSD patients traumatized at an air show plane crash in 1988 (Ramstein, Germany).
In human studies, the amygdala has been shown to be strongly involved in the formation of emotional memories, especially fear-related memories. Neuroimaging studies in humans have revealed both morphological and functional aspects of PTSD.
The amygdalocentric model of PTSD proposes that it is associated with hyperarousal of the amygdala and insufficient top-down control by the medial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus particularly during extinction. This is consistent with an interpretation of PTSD as a syndrome of deficient extinction ability. Further animal and clinical research into the amygdala and fear conditioning may suggest additional treatments for the condition.
Genetics
There is evidence that susceptibility to PTSD is hereditary. For twin pairs exposed to combat in Vietnam, having a monozygotic (identical) twin with PTSD was associated with an increased risk of the co-twin having PTSD compared to twins that were dizygotic (non-identical twins).
Recently, it has been found that several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in FK506 binding protein 5 (FKBP5) interact with childhood trauma to predict severity of adult PTSD. These findings suggest that individuals with these SNPs who are abused as children are more susceptible to PTSD as adults.
This is particularly interesting given that FKBP5 SNPs have previously been associated with peritraumatic dissociation (that is, dissociation at the time of the trauma), which has itself been shown to be predictive of PTSD. Furthermore, FKBP5 may be less expressed in those with current PTSD. Another recent study found a single SNP in a putative estrogen response element on ADCYAP1R1 (encodes pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type I receptor or PAC1) to predict PTSD diagnosis and symptoms in females. Incidentally, this SNP is also associated with fear discrimination. The study suggests that perturbations in the PACAP-PAC1 pathway are involved in abnormal stress responses underlying PTSD.
Risk factors
Although most people (50-90%) encounter trauma over a lifetime, only about 8% develop full PTSD. Vulnerability to PTSD presumably stems from an interaction of biological diathesis, early childhood developmental experiences, and trauma severity.
Predictor models have consistently found that childhood trauma, chronic adversity, and familial stressors increase risk for PTSD as well as risk for biological markers of risk for PTSD after a traumatic event in adulthood. This effect of childhood trauma, which is not well understood, may be a marker for both traumatic experiences and attachment problems. Proximity to, duration of, and severity of the trauma also make an impact; and interpersonal traumas cause more problems than impersonal ones.
Military experience
Schnurr, Lunney, and Sengupta identified risk factors for the development of PTSD in Vietnam veterans. Among those are:
- Hispanic ethnicity, coming from an unstable family, being punished severely during childhood, childhood asocial behavior and depression as pre-military factors
- War-zone exposure, peritraumatic dissociation, depression as military factors
- Recent stressful life events, post-Vietnam trauma and depression as post-military factors
They also identified certain protective factors, such as:
- Japanese-American ethnicity, high school degree or college education, older age at entry to war, higher socioeconomic status and a more positive paternal relationship as pre-military protective factors
- Social support at homecoming and current social support as post-military factors. Other research also indicates the protective effects of social support in averting PTSD or facilitating recovery if it develops.
There may also be an attitudinal component; for example, a soldier who believes that they will not sustain injuries may be more likely to develop symptoms of PTSD than one who anticipates the possibility, should either be wounded. Likewise, the later incidence of suicide among those injured in home fires above those injured in fires in the workplace suggests this possibility.
Foster care
In the Casey Family Northwest Alumni Study, conducted in conjunction with researchers from the Harvard Medical School in Oregon and Washington state, the rate of PTSD in adults who were in foster care for one year between the ages of 14-18 was found to be higher than that of combat veterans. Up to 25 percent of those in the study meet the diagnostic criteria for PTSD as compared to 12-13 percent of Iraq war veterans and 15 percent of Vietnam War veterans, and a rate of 4 percent in the general population. The recovery rate for foster home alumni was 28.2% as opposed to 47% in the general population.
In one study (Dubner and Motta, 1999), 60% of children in foster care who had experienced sexual abuse had PTSD, and 42% of those who had been physically abused fulfilled the PTSD criteria. PTSD was also found in 18% of the children who were not abused. These children may have developed PTSD due to witnessing violence in the home, or as a result of real or perceived parental abandonment.
Diagnosis
Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for PTSD, stipulated in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV (Text Revision) (DSM-IV-TR), may be summarized as:
A: Exposure to a traumatic event
This must have involved both (a) loss of “physical integrity”, or risk of serious injury or death, to self or others, and (b) a response to the event that involved intense fear, horror or helplessness (or in children, the response must involve disorganized or agitated behavior). (The DSM-IV-TR criterion differs substantially from the previous DSM-III-R stressor criterion, which specified the traumatic event should be of a type that would cause “significant symptoms of distress in almost anyone,” and that the event was “outside the range of usual human experience.”)
B: Persistent re-experiencing
One or more of these must be present in the victim: flashback memories, recurring distressing dreams, subjective re-experiencing of the traumatic event(s), or intense negative psychological or physiological response to any objective or subjective reminder of the traumatic event(s).
C: Persistent avoidance and emotional numbing
This involves a sufficient level of:
- avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma, such as certain thoughts or feelings, or talking about the event(s);
- avoidance of behaviors, places, or people that might lead to distressing memories;
- inability to recall major parts of the trauma(s), or decreased involvement in significant life activities;
- decreased capacity (down to complete inability) to feel certain feelings;
- an expectation that one’s future will be somehow constrained in ways not normal to other people.
D: Persistent symptoms of increased arousal not present before
These are all physiological response issues, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, or problems with anger, concentration, or hypervigilance.
E: Duration of symptoms for more than 1 month
If all other criteria are present, but 30 days have not elapsed, the individual is diagnosed with Acute stress disorder.
F: Significant impairment
The symptoms reported must lead to “clinically significant distress or impairment” of major domains of life activity, such as social relations, occupational activities, or other “important areas of functioning”.
Since the introduction of DSM-IV, the number of possible events which might be used to diagnose PTSD has increased; one study suggests that the increase is around 50%. Various scales exist to measure the severity and frequency of PTSD symptoms. Standardized screening tools such as Trauma Screening Questionnaire and PTSD Symptom Scale can be used to detect possible symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.
Research-based alternative symptom groups
Emerging factor analytic research suggests that PTSD symptoms group empirically into four clusters, not the three currently described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. One model supported by this research divides the traditional avoidance symptoms into a cluster of numbing symptoms (such as loss of interest and feeling emotionally numb) and a cluster of behavioral avoidance symptoms (such as avoiding reminders of the trauma). An alternative model adds a fourth cluster of dysphoric symptoms. These include symptoms of emotional numbing, as well as anger, sleep disturbance, and difficulty concentrating (traditionally grouped under the hyperarousal cluster).
DSM-5 proposed diagnostic criteria changes
In preparation for the May 2013 release of the DSM-5, the fifth version of the American Psychiatric Association’s diagnostic manual, draft diagnostic criteria was released for public comment, followed by a two-year period of field testing. Proposed changes to the criteria include:
- Criterion A (prior exposure to traumatic events) is more specifically stated, and evaluation of an individual’s emotional response at the time (current criterion A2) is dropped.
- Several items in Criterion B (intrusion symptoms) are rewritten to add or augment certain distinctions now considered important.
- Special consideration is given to developmentally appropriate criteria for use with children and adolescents. This is especially evident in the restated Criterion B – intrusion symptoms. Development of age-specific criteria for diagnosis of PTSD is ongoing at this time.
- Criterion C (avoidance and numbing) has been split into “C” and “D”:
- Criterion C (new version) now focuses solely on avoidance of behaviors or physical or temporal reminders of the traumatic experience(s). What were formerly two symptoms are now three, due to slight changes in descriptions.
- New Criterion D focuses on negative alterations in cognition and mood associated with the traumatic event(s), and contains two new symptoms, one expanded symptom, and four largely unchanged symptoms specified in the previous criteria.
- Criterion E (formerly “D”), which focuses on increased arousal and reactivity, contains one modestly revised, one entirely new, and four unchanged symptoms.
- Criterion F (formerly “E”) still requires duration of symptoms to have been at least one month.
- Criterion G (formerly “F”) stipulates symptom impact (“disturbance”) in the same way as before.
- The “acute” vs “delayed” distinction is dropped; the “delayed” specifier is considered appropriate if clinical symptom onset is no sooner than 6 months after the traumatic event(s).
“Developmental trauma disorder”, a proposed new diagnosis, was still under discussion at the time of the draft publication.
Public policy response
In recent history, catastrophes (by human means or not) such as the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami may have caused PTSD in many survivors and rescue workers. Today relief workers from organizations such as the Red Cross and the Salvation Army provide counseling after major disasters as part of their standard procedures to curb severe cases of posttraumatic stress disorder.
United States
A review of the provision of compensation to veterans for PTSD by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs began in 2005 after the VA had noted a 30% increase in PTSD claims in recent years. This led to a backlash from veterans’-rights groups, and to some highly publicized suicides by veterans who feared losing their benefits, which in some cases constituted their only income. In response, on November 10, 2005, the Secretary of Veterans Affairs announced that “the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) will not review the files of 72,000 veterans currently receiving disability compensation for posttraumatic stress disorder…”
The diagnosis of PTSD in U.S. military veterans has been a subject of some controversy due to uncertainties in objectively diagnosing PTSD in those who may have been exposed to trauma, and due to this diagnosis’ association with some incidence of compensation-seeking behavior.
Many veterans of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan returning home have faced significant physical, emotional and relational disruptions. In response, the United States Marine Corps has instituted programs to assist them in re-adjusting to civilian life, especially in their relationships with spouses and loved ones, to help them communicate better and understand what the other has gone through. Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) developed the Battlemind program to assist service members avoid or ameliorate PTSD and related problems.
Other countries
In the UK, there has been some controversy that National Health Service is dumping veterans on service charities like Combat Stress.
Veterans Affairs Canada offers a new program that includes rehabilitation, financial benefits, job placement, health benefits program, disability awards and family support.
Management
Prevention and early intervention strategies
Modest benefits have been seen from early access to cognitive behavioral therapy, as well as from some medications such as propranolol. Critical incident stress management has been suggested as a means of preventing PTSD but subsequent studies suggest the likelihood of its producing iatrogenic outcomes. A review of multiple studies confirmed the finding of no benefit to trauma survivors from single-session early-response interventions, as well as a failure of blanket multiple-session prevention interventions to yield a benefit to all participants (some were even harmed).
Early detection
The ability to prescreen individuals would be of great help in getting treatment to those who are at risk of PTSD prior to development of the syndrome. Several biological indicators have been identified that are related to later PTSD development. First, Delhanty found that higher response times and a smaller hippocampal volume were identified as linked to later PTSD development. However, both of these indicators are relatively difficult to test for and need specialized tests and or equipment to identify. A blood biomarker is much easier to test for. Van Zuiden et al. found just such a biomarker when testing U.S. Army soldiers prior to deployment. They found that soldiers with more glucocorticoid receptors (GR) were more likely to be diagnosed with PTSD six months after deployment. However, higher GR levels have not been identified as a cause of PTSD, and may instead be an intermediator, or even an indicator that the individual has previously experienced traumatic events. There is a great deal of overlap between high GR levels and those who later are diagnosed with and without PTSD. Thus, the identification of high GR is simply a vulnerability indicator at this time.
Delhanty found that biological precursors existed directly following traumatic exposure in those who later developed chronic PTSD and were significantly different from those who did not. Directly following the traumatic event later sufferers often have significantly lower levels of hypothalamic pituitary-adrenal activity and a corresponding decrease in Cortisol. Other methods of early detection include the identification of specific risk factors associated with later PTSD symptoms. Resnick, Acierno, Holmes, Kilpatrick, and Jager for example were able to identify that the forensic exam given to victims after a rape was associated with PTSD. Finally, global treatments attempt to avoid the problems of early detection by simply treating everyone involved. However, many studies have found this to be often ineffective and for global treatments to at times increase prevalence rates of PTSD.
Preventive Treatments
Psychological debriefing
The first form of preventive treatment is that of a psychological debriefing. Psychological debriefing is the most often used preventive measure. One of the main reasons for this is the relative ease with which this treatment can be given to individuals directly following an event. It consists of interviews that are meant to allow individuals to directly confront the event and share their feelings with the counselor and to help structure their memories of the event. However, while this form of therapy is the most often used it is actually the least effective. Studies have had mixed findings concerning psychological debriefings and have ranged from being of significant help to helping in the formation of PTSD in individuals who would otherwise have not developed PTSD. The greater number of studies tends to simply find that it is neither overly beneficial nor harmful.
Risk Targeted Interventions
Risk targeted interventions are those that attempt to mitigate specific formative information or events. It can target modeling normal behaviors, instruction on a task or giving information on the event. For example, rape victims were given an instruction video on the procedures for a forensic exam. Also included in the video was advice on how to identify and stop avoidance behavior and control anxiety. Finally, the individuals modeling the forensic exam were shown to be calm and relaxed. PTSD diagnosis for those who saw the video were thirty three percent less than for those who went through the standard forensic procedure.
Psychobiological Treatments
Psychobiological treatments have also found success, especially with cortisol. Psychobiological treatments target biological changes that occur after a traumatic event. They also attempt to chemically alter learning or memory formation. Cortisol treatments after a traumatic event have found success in mitigating later diagnosis of PTSD. As discussed earlier Cortisol is often lower in individuals who are at risk of PTSD after a traumatic event than their counterparts. By increasing cortisol levels to normal levels this has been shown to reduce arousal post event as well prevent GR upregulation.
Stepped Collaborative Care
Stepped collaborative care is where individuals who are at risk are monitored for symptoms. As symptoms of PTSD appear the level of care is increased to treat those symptoms.
Psychotherapeutic interventions
Many forms of psychotherapy have been advocated for trauma-related problems such as PTSD. Basic counseling practices common to many treatment responses for PTSD include education about the condition and provision of safety and support.
The psychotherapy programs with the strongest demonstrated efficacy include cognitive behavioral programs, variants of exposure therapy, stress inoculation training (SIT), variants of cognitive therapy (CT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and many combinations of these procedures. A 2010 review disagrees that these treatments have proven efficacy, and points out methodological flaws in the studies and previous meta-analyses.
EMDR or trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TFCBT) was recommended as first-line treatments for trauma victims in a 2007 review; however, “the evidence base [for EMDR] was not as strong as that for TFCBT … Furthermore, there was limited evidence that TFCBT and EMDR were superior to supportive/non-directive treatments, hence it is highly unlikely that their effectiveness is due to non-specific factors such as attention.” A meta-analytic comparison of EMDR and cognitive behavioral therapy found both protocols indistinguishable in terms of effectiveness in treating PTSD; however “the contribution of the eye movement component in EMDR to treatment outcome” is unclear.
Behavioral and Cognitive Behavioral therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) seeks to change the way a trauma victim feels and acts by changing the patterns of thinking and/or behavior responsible for negative emotions. CBT have been proven to be an effective treatment for PTSD, and is currently considered the standard of care for PTSD by the United States Department of Defense In CBT, individuals learn to identify thoughts that make them feel afraid or upset, and replace them with less distressing thoughts. The goal is to understand how certain thoughts about cause PTSD-related stress.
Recent research on contextually based third-generation behavior therapies suggests that they may produce results comparable to some of the better validated therapies. Many of these therapy methods have a significant element of exposure, and have demonstrated success in treating the primary problems of PTSD and co-occurring depressive symptoms.
Exposure therapy is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy that involves assisting trauma survivors to re-experience distressing trauma-related memories and reminders in order to facilitate habituation and successful emotional processing of the trauma memory. Most exposure therapy programs include both imaginal confrontation with the traumatic memories and real-life exposure to trauma reminders; this therapy modality is well supported by clinical evidence. Indeed, the success of exposure-based therapies has raised the question of whether exposure is a necessary ingredient in the treatment of PTSD. Some organizations have endorsed the need for exposure. The US Department of Veterans Affairs has been actively training mental health treatment staff in Prolonged Exposure Therapy and Cognitive Processing Therapy in an effort to better treat US Veterans with PTSD.
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is specifically targeted as a treatment for PTSD. Based on the evidence of controlled research, the American Psychiatric Association and the United States Department of Veterans Affairs and Department of Defense have placed EMDR in the highest category of effectiveness and research support in the treatment of trauma. Several international bodies have made similar recommendations. However, some reviewers no longer believe that the eye movements assist in recovery, proposing instead that the review of and engagement with memories, processing of cognitions, and rehearsal of coping skills are the psychotherapeutically effective components of the procedure.
Interpersonal psychotherapy
Other approaches, particularly involving social supports, may also be important. An open trial of interpersonal psychotherapy reported high rates of remission from PTSD symptoms without using exposure. A current, NIMH-funded trial in New York City is now (and into 2013) comparing interpersonal psychotherapy, prolonged exposure therapy, and relaxation therapy.
Medication
A variety of medications has shown adjunctive benefit in reducing PTSD symptoms, but “there is no clear drug treatment for PTSD”. Positive symptoms (re-experiencing, hypervigilance, increased arousal) generally respond better to medication than negative symptoms (avoidance, withdrawal), and it is recommended that any drug trial last for at least 6–8 weeks.
Symptom management: potentially useful medication classes
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors). SSRIs are considered to be a first-line drug treatment. SSRIs for which there are data to support use include: citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline.
Among the anti-depressants described in this section, bupropion and venlafaxine have the lowest patient drop-out rates. Sertraline, fluoxetine, and nefazodone have a modestly higher drop-out rate (~15%), and the heterocyclics and paroxetine have the highest rates (~20%+). Where drop-out is caused or feared because of medication side-effects, it should be remembered that most patients do not experience such side-effects.
Alpha-adrenergic antagonists. Prazosin (“Minipress”), in a small study of combat veterans, has shown substantial benefit in relieving or reducing nightmares. Clonidine (“Catapres”) can be helpful with startle, hyperarousal, and general autonomic hyperexcitability.
Anti-convulsants, mood stabilizers, anti-aggression agents. Carbamazepine (“Tegretol”) has likely benefit in reducing arousal symptoms involving noxious affect, as well as mood or aggression. Topiramate (“Topamax”) has been effective in achieving major reductions in flashbacks and nightmares, and no reduction of effect was seen over time. Zolpidem (“Ambien”) has also proven useful in treating sleep disturbances.
Lamotrigine (“Lamictal”) may be useful in reducing reexperiencing symptoms, as well as avoidance and emotional numbing. Valproic acid (“Depakene”) and has shown reduction of symptoms of irritability, aggression, and impulsiveness, and in reducing flashbacks. Similarly, lithium carbonate has worked to control mood and aggressions (but not anxiety) symptoms. Buspirone (“BuSpar”) has an effect similar to that of lithium, with the additional benefit of working to reduce hyperarousal symptoms.
Antipsychotics. Risperidone can be used to help with dissociation, mood issues, and aggression.
Atypical antidepressants. Nefazodone (“Serzone”) can be effective with sleep disturbance symptoms, and with secondary depression, anxiety, and sexual dysfunction symptoms. Trazodone (“Desyrel”) can also reduce or eliminate problems with disturbed sleep, and with anger and anxiety.
Beta blockers. Propranolol (“Inderal”) has demonstrated possibilities in reducing hyperarousal symptoms, including sleep disturbances.
Benzodiazepines. These can be used with caution for short-term anxiety relief, hyperarousal, and sleep disturbance. While benzodiazepines can alleviate acute anxiety, there is no consistent evidence that they can stop the development of PTSD, or are at all effective in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Additionally benzodiazepines may reduce the effectiveness of psychotherapeutic interventions and there is some evidence that benzodiazepines may contribute to the development and chronification of PTSD. Other drawbacks include the risk of developing a benzodiazepine dependence and withdrawal syndrome; additionally individuals with PTSD are at an increased risk of abusing benzodiazepines.
Glucocorticoids. Additionally, post-stress high dose corticosterone administration was recently found to reduce ‘PTSD-like’ behaviors in a rat model of PTSD. In this study, corticosterone impaired memory performance, suggesting that it may reduce risk for PTSD by interfering with consolidation of traumatic memories. The neurodegenerative effects of the glucocorticoids, however, may prove this treatment counterproductive.
Heterocyclic / Tricyclic anti-depressants anti-depressants. Amitriptyline (“Elavil”) has shown benefit for positive distress symptoms, and for avoidance, and Imipramine (“Tofranil”) has shown benefit for intrusive symptoms.
Monoamine-oxidase inhibitors (MAOs). Phenelzine (“Nardil”) has for some time been observed to be effective with hyperarousal and depression, and is especially effective with nightmares.
Miscellaneous other medications. Clinical trials evaluating methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “Ecstasy”) in conjunction with psychotherapy are being conducted in Switzerland and Israel.
Symptom prevention: potentially useful medication classes
Some medications have shown benefit in preventing PTSD or reducing its incidence, when given in close proximity to a traumatic event. These medications include:
Alpha-adrenergic antagonists. Anecdotal report of success in using clonidine (“Catapres”) to reduce traumatic stress symptoms suggests that it may have benefit in preventing PTSD.
Beta blockers. Propranolol (“Inderal”), similarly to clonidine, may be useful if there are significant symptoms of “over-arousal”. These may inhibit the formation of traumatic memories by blocking adrenaline’s effects on the amygdala.
Glucocorticoids. There is some evidence suggesting that administering glucocorticoids immediately after a traumatic experience may help prevent PTSD. Several studies have shown that individuals who receive high doses of hydrocortisone for treatment of septic shock, or following surgery, have a lower incidence and fewer symptoms of PTSD.
Opiates. In a retrospective analysis of combat injury field data for US troops in Iraq, it was found that those who received morphine in the early stages of their treatment had a significantly lower rate of subsequent PTSD, when compared with those who did not receive morphine at that time.
Medication and self-medication issues and risks with PTSD
Alcohol abuse and drug abuse commonly co-occur with PTSD. Recovery from posttraumatic stress disorder or other anxiety disorders may be hindered, or the condition worsened, by medication or substance overuse, abuse, or dependence; resolving these problems can bring about a marked improvement in an individual’s mental health status and anxiety levels.
Benzodiazepines are risky in several ways. They can be especially addictive when PTSD is present, and this is especially true with the fast-acting ones. Dis-inhibition upon initiation of treatment is another risk with this medication class. Finally, termination of the drug can be especially difficult. Recovery from benzodiazepine abuse or dependence tends to take a lot longer than recovery from alcohol abuse or dependence, but people can regain their previous good health. PTSD symptoms may temporarily worsen however, during alcohol withdrawal or benzodiazepine withdrawal.
Yohimbine (not considered specifically appropriate for PTSD) increases arousal by increasing release of endogenous norepinephrine, and can worsen PTSD symptoms.
Epidemiology
There is debate over the rates of PTSD found in populations, but despite changes in diagnosis and the criteria used to define PTSD between 1997 and 2007, epidemiological rates have not changed significantly.
International PTSD rates
The United Nations’ World Health Organization publishes estimates of PTSD impact for each of its member states; the latest data available are for 2004. Considering only the 25 most populated countries, ranked by overall age-standardized Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY) rate, the top half of the ranked list is dominated by Asian/Pacific countries, the USA, and Egypt. Ranking the countries by the male-only or female-only rates produces much the same result, but with less meaningfulness, as the score range in the single sex rankings is much reduced (4 for women, 3 for men, as compared with 14 for the overall score range), suggesting that the differences between female and male rates, within each country, is what drives the distinctions between the countries.
United States
The National Comorbidity Survey has estimated that the lifetime prevalence of PTSD among adult Americans is 7.8%, with women (10.4%) twice as likely as men (5%) to have PTSD at some point in their lives.
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs estimates that 830,000 Vietnam War veterans suffered symptoms of PTSD. The National Vietnam Veterans’ Readjustment Study (NVVRS) found 15.2% of male and 8.5% of female Vietnam Vets to suffer from current PTSD at the time of the study. Life-Time prevalence of PTSD was 30.9% for males and 26.9% for females. In a reanalysis of the NVVRS data, along with analysis of the data from the Matsunaga Vietnam Veterans Project, Schnurr, Lunney, Sengupta, and Waelde found that, contrary to the initial analysis of the NVVRS data, a large majority of Vietnam veterans suffered from PTSD symptoms (but not the disorder itself). Four out of five reported recent symptoms when interviewed 20–25 years after Vietnam.
In other species
There have been reports of captive and wild elephants suffering from posttraumatic stress reactions, the latter from seeing members of their herd shot by hunters. Service dogs used overseas in the military have been said to develop posttraumatic stress after witnessing war.
History
Earliest reports
Reports of battle-associated stress reactions appear as early as the 6th century BC/BCE. One of the first descriptions of PTSD was made by the Greek historian Herodotus. In 490 BC/BCE he described, during the Battle of Marathon, an Athenian soldier who suffered no injury from war but became permanently blind after witnessing the death of a fellow soldier.
Modern recognition in military settings
In the early 19th century military medical doctors started diagnosing soldiers with “exhaustion” after the stress of battle. This “exhaustion” was characterized by mental shutdown due to individual or group trauma. Soldiers during the 19th century were not supposed to be scared or show any fear in the midst of battle. The only treatment for this “exhaustion” was to bring the afflicted to the back for a bit then send them back into battle. During the intense and frequently repeated stress, the soldiers became fatigued as a part of their body’s natural shock reaction.
According to Stéphane Audoin-Rouzeau and Annette Becker, “One-tenth of mobilized American men were hospitalized for mental disturbances between 1942 and 1945, and after thirty-five days of uninterrupted combat, 98% of them manifested psychiatric disturbances in varying degrees.”
Although PTSD-like symptoms have also been recognized in combat veterans of many military conflicts since, the modern understanding of PTSD dates from the 1970s, largely as a result of the problems that were still being experienced by US military veterans of the war in Vietnam.
Previous diagnoses now considered historical equivalents of PTSD include railway spine, stress syndrome, shell shock, battle fatigue, or traumatic war neurosis.
Terminology
The term post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) was coined in the mid 1970s, in part through the efforts of anti-Vietnam War activists and the anti war group Vietnam Veterans Against the War and Chaim F. Shatan, who worked with them and coined the term post-Vietnam Syndrome; the condition was added to the DSM-III as posttraumatic stress disorder.
Early in 1978, the term was used in a working group finding presented to the Committee of Reactive Disorders. The term was formally recognized in 1980. (In the authoritative DSM-IV, the spelling “posttraumatic stress disorder” is used. Elsewhere, “posttraumatic” is often rendered as two words — “post-traumatic stress disorder” or “post traumatic stress disorder” — especially in less formal writing on the subject.)
